Powerful electrodynamic heads from branded manufacturers are highly valued by true music lovers. During operation, various troubles can occur with the speakers. Most often, the coil breaks or the integrity of the diffuser is damaged, up to its complete destruction. Since you don’t want to lose excellent speakers, many are interested in how to make a diffuser for a speaker at home.
Powerful loudspeakers used in professional concert equipment have replaceable diffusers, and the entire process of replacing them is well established.
Where to buy an acoustic diffuser
The Echo Design company offers to buy acoustic diffusers. To make them, craftsmen use high quality materials. Most often, birch wood is used, since this particular species is famous for its excellent acoustic characteristics. The aesthetic appearance of birch becomes another reason to buy acoustic diffusers. People who are not familiar with the true purpose of diffusers may mistake them for a part of a fashionable interior. The diffusers really look original. The structure is divided into a certain number of sections of different depths. This provides a diffuse but controlled reflection of sound waves into the room. For the first time, an acoustic wooden diffuser was assembled by the German physicist Manfred Schröder. His invention is still associated with the name of the creator.
Making a speaker diffuser with your own hands
When repairing and restoring some models of loudspeakers, you may need to make an aluminum speaker cone yourself. For such a product, you will need aluminum foil of appropriate thickness and a mandrel on which the workpiece will be molded. The mandrel can be made from gypsum powder or wood. A wooden mandrel will require more manufacturing time, but is easier to shape. It is also more convenient to mold the configuration of the future product. Using the technology of using a punch and a matrix, you can experiment with various materials. Speaker diffusers can be made from fabric impregnated with varnish, polymer materials and even wood.
Schrader diffuser
| A Schroeder diffuser is a design whose main purpose is to disperse sound in a room. The scientist devoted many years to the study of acoustics. He explored sound in Europe's most famous concert halls. Acoustic diffusers provide a high degree of sound wave dispersion in a wide range of frequencies at any angle of incidence. |
An acoustic diffuser shifts in space and delays in time the early reflections of the surfaces that enclose the room. Modern acoustic diffusers are still created based on the ideas about three-dimensional diffusion of sound waves, which Mr. Schroeder once preached. The designs presented in our acoustic diffuser store can be installed in various rooms. Diffusers can be combined with sound absorbers and bass traps. If you dream of ideal sound and need an acoustic diffuser, you can buy it in the Echo Design showroom.
Manfred Schröder
0
The catalyst for the widespread use of acoustic diffusers was the ideas and developments of Manfred Schroeder, professor of physics at the University of Göttingen (Germany), who published in 1975 his fundamental work on the topic of diffuse reflections from surfaces built on the principle of a mathematical sequence of maximum length
0
In the 1970s Manfred Schröder and his colleagues studied more than 20 famous European concert halls. It turned out that listeners perceive sound in long halls better than in wide ones. Schroeder connected this with his other observation that the viewer is more pleasant to listen to slightly different signals entering the left and right ears than to listen to absolutely identical ones.
0
In wide halls, early reflections reach the listener from the ceiling. These reflections produce very similar signals for the left and right ears. In narrower and longer halls, the first reflected signals arrive at the listener from the side walls and are quite different from each other. This may be why many modern concert halls have unsatisfactory acoustic characteristics. They prefer to make the halls wider to accommodate more seats, and low ceilings are preferable for modern air conditioning systems. To improve the acoustics of such halls, reflections from the ceiling had to be redirected towards the walls. After conducting a number of studies, Manfred Schröder proposed an original sound-diffusing design, later called the Schröder diffuser, to solve this problem.
Operating principle of an acoustic diffuser
Let's not hope that you understand absolutely all of the above, because for unprepared people it may indeed look somewhat complicated. Let's try to explain the principle by which an acoustic wooden diffuser works. Imagine an ocean wave crashing against a rock. It is similar to a sound wave with a certain vector of movement. When a wave hits a rock, the energy is reflected in hundreds or millions of splashes. It does not disappear anywhere, but returns and dissipates. The role of the rock in this case is played by an acoustic diffuser. Buying such a thing for your music studio means creating excellent acoustics.
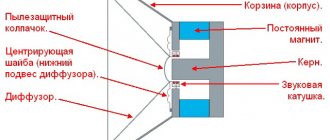
Making a passive radiator
It is good to use a full-fledged head as a passive radiator.
An idea of the design of a passive radiator installed next to a loudspeaker is shown in Fig. 3, which shows how an additional weight in the form of a disk is attached in the center of the diffuser with a bolt and nuts.
Rice. 3. Appearance of the speaker and its passive radiator.
The hole in the diffuser is sealed with a piece of hard paper (whatman paper or thin cardboard) with teeth glued to the diffuser (see Fig. 4) with celluloid or other glue, for example BF-2. It goes without saying that the fundamental resonant frequency of a loudspeaker designed for a passive radiator does not matter at all.
Rice. 4. Seal the hole in the diffuser after removing the coil.
Or you can buy it on Aliexpress. Here for $3.4 or here for $10.5.
When designing a bass reflex with a closed hole, you should not make it less than 30–40 liters in volume with a resonant frequency below 50 Hz, because an increase in the mass of the passive moving system, as well as the mass of air in the passage of a conventional FI, worsens the transient characteristics of the loudspeaker.
Criteria for selecting acoustic diffusers
Before purchasing an acoustic diffuser, you need to analyze the space in which it will be installed. It is important to understand the main purpose of the room and its volume. If we take the average formula for calculations, then we will need one acoustic diffuser per cube of the room. The basic criteria for choosing acoustic diffusers are clear, but we should not forget about their correct installation. Experts recommend mounting acoustic diffusers according to the “dead/living corner” principle. The live corner is where the listener is, and the dead corner is located behind the sound source. They should be located opposite each other.
Calculation of a passive radiator
Another positive quality of a bass reflex with a closed hole is a slightly greater in-phase movement of both diffusers in the resonance region compared to the movement of the air volume in the hole and the speaker cone in a conventional bass reflex. The resonant frequency of a bass reflex with a closed hole is equal (as well as a conventional one):
where mf is the mass of the moving system of the passive radiator plus the mass of air oscillating with it and attached to the diffuser, g; Sf is the resulting flexibility (the reciprocal of elasticity) of the volume of air in the box and the additional moving system, cm/din.
The calculation of a bass reflex with a closed hole is carried out as follows: by choosing the volume of the box Vf and knowing the effective diameter of the diffuser of the passive radiator Deff, determine the flexibility of the air volume from the expression:
Here the volume of the box Vph is expressed in cm3, and the effective diameter of the diffuser of the passive radiator Deff is in cm. Let us recall that the effective diameter of the diffuser is Deff = 0.85–0.9 Ddif, where Ddiff is the total diameter of the diffuser.
The equivalent effective diameter of an elliptical (oval) diffuser is:
where Db is the large diameter and Dm is the small diameter of the ellipse. Since the flexibility of the diffuser suspension of the passive radiator Spod is much greater than the flexibility of the air volume of the box Sf, its influence on the total flexibility is extremely small and can be neglected.
Overall flexibility is determined by the formula:
And when Spod>>Cf, Commun≈Cf.
Taking, as usual, the resonant frequency of a closed phase inverter equal to the main resonant frequency of the loudspeaker, find the mass of the MF corresponding to this frequency and the flexibility of the selected volume:
As mentioned above, this mass includes the mass of the passive radiator diffuser mrad and the added mass of air oscillating with it Δm, i.e. mf = mrad + Δm. The value of Δm depends on the effective diameter of the diffuser and is determined by the expression Δm = 8*10-4D3eff g. Thus, the radiator diffuser must have a mass mrad = mph – Δm; Practically this value will be equal to the mass of the load that needs to be installed on the diffuser. To facilitate the necessary calculations, the table shows the values of volume flexibility Cf for boxes with a volume of 20 to 80 liters and passive radiator diffusers with an effective diameter of 15 to 22 cm, and also indicates the value of the attached air mass Δm for the same diffuser diameters.
| Vf, l | Flexibility of box volume, cm/din 10-6 at Def, cm | ||||||
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | |
| Δ m, g | 1,7 | 3,3 | 3,9 | 4,7 | 5,5 | 6,4 | 8,6 |
| 20 | 0,45 | 1,35 | 0,27 | 0,22 | 0,17 | 0,14 | 0,1 |
| 30 | 0,67 | 0,52 | 0,41 | 0,32 | 0,26 | 0,24 | 0,15 |
| 40 | 0,9 | 0,69 | 0,55 | 0,43 | 0,35 | 0,29 | 0,19 |
| 50 | 1,12 | 0,87 | 0,68 | 0,54 | 0,44 | 0,366 | 0,24 |
| 60 | 0,35 | 1,04 | 0,82 | 0,65 | 0,52 | 0,43 | 0,29 |
| 70 | 1,57 | 1,21 | 0,95 | 0,76 | 0,61 | 0,5 | 0,34 |
| 80 | 1,8 | 1,4 | 1,09 | 0,87 | 0,7 | 0,57 | 0,39 |
The flexibility value of the air volume in boxes with intermediate values and the effective diameter of the radiator diffuser is determined by interpolation using two adjacent flexibility values, between which the accepted dimensions are located.
For example, let’s determine the mass of the load that must be mounted on a passive radiator diffuser with a diameter of Ddif=22 cm, installed in a FI box with a volume of Vph=50 liters at a resonant frequency of FI of 45 Hz. Effective diameter Def=0.87* Ddiff=0.87*22=19 cm. Using the table, we find the flexibility of the air volume in the box with such an effective diffuser diameter; this flexibility is equal to Sf=0.44*10-6 cm/din. The total mass of the diffuser should be:
The added mass of air, according to the table, is equal to Δm = 5.5 g. Therefore, to obtain a given resonant frequency, it is necessary to install an additional weight mrad = mf – Δm = 28.4-5.5 ≈ 23 g. The additional weight is steel or copper (brass) disk with thickness h, which for steel, depending on the diameter of the disk d, is equal to
As stated above, the magnetic system and centering washer are removed from the speaker designed to function as a passive radiator. This is done in order to increase the flexibility and linearity of the movement of the moving system, and eliminate the danger of touching the voice coil.
This does not reduce the effective volume of the box.
Acoustic polystyrene foam panel
Experienced professionals prefer acoustic diffusers made of wood. According to the majority, they are valuable for their naturalness and correct reflection of the sound that was developed by nature itself. Some connoisseurs of ideal sound are more impressed by the acoustic polystyrene foam panel, but this is not due to the sound characteristics. Economical price plays a decisive role here. An acoustic polystyrene foam panel is almost 2 times cheaper than a wooden diffuser. Another advantage of acoustic diffusers made of polystyrene foam is the variety of color options. You can create a stylish and bright interior.
However, what is proper acoustics?
0
The acoustics of a room, depending on the purpose of its use, should provide optimal conditions for the listener to perceive sound. For example, for optimal enjoyment of live chamber music, the room acoustics must have a very high reverberation time. Whereas the acoustics of a television studio, for example, should provide the dryest possible sound, with very low reverberation times
×
0
To develop the acoustic design of special rooms, acoustic engineers have only 3 tools at their disposal: absorption, reflection and dispersion (diffusion) of sound energy. Sound-absorbing panels and sound-reflecting surfaces (flat or curved) have become quite widespread today. But the use of sound absorption and reflection techniques alone cannot solve some of the acoustic problems that arise in small studio spaces or in disproportionately wide concert halls.
Acoustic diffuser calculator
Before purchasing and installing, you need to calculate the acoustic diffuser. It is required to know the required depth and width of the cells, as well as the boundaries of the effective frequency range. To get the correct figures, experts use an acoustic diffuser calculator. Buyers who do not have experience in this area are better off turning to professionals. Using an acoustic diffuser calculator, Echo Design specialists will make accurate calculations and help you decide on the choice of module. You can only use the acoustic diffuser calculator yourself if you are absolutely confident in your skills. Calculating an acoustic diffuser requires a deep understanding of the topic.
Schroeder diffuser
0
In wide halls, early reflections reach the listener from the ceiling. These reflections produce very similar signals for the left and right ears. In narrower and longer halls, the first reflected signals arrive at the listener from the side walls and are quite different from each other. This may be why many modern concert halls have unsatisfactory acoustic characteristics. They prefer to make the halls wider to accommodate more seats, and low ceilings are preferable for modern air conditioning systems. To improve the acoustics of such halls, reflections from the ceiling had to be redirected towards the walls. After conducting a number of studies, Manfred Schröder proposed an original sound-diffusing design, later called the Schröder diffuser, to solve this problem.
Advantages of acoustic diffusers from Echo Design:
- Environmental friendliness. Only natural raw materials are used as materials for the manufacture of acoustic diffusers.
- Efficiency. Our diffusers operate in the range from 580 to 8000 Hz.
- Practicality. Our acoustic diffusers can also be used as decoration.
- Reliability. The modules are made of high quality and are highly durable.
If you need an acoustic diffuser, you can buy a decent copy in our showroom. Experienced specialists will provide consultation and necessary calculations and help you buy an acoustic diffuser that will satisfy all the customer’s needs.
Homemade speaker diffuser
The resulting ready-made mixture is applied to a plaster mold in an arbitrary manner. The number of layers between the punch and the matrix depends on the source raw materials, plant components and is selected experimentally. The paper pulp must be applied one layer at a time and left until completely dry, so the manufacturing process can take 4-5 days. When leveling the mixture, small unevenness may appear on the finished product. This will not affect the quality of the future product in any way. The workpiece can be painted with black varnish or ink. To restore the speaker, you will also need to make a suspension.