Greetings to all readers! Anyone who has ever chosen a speaker system has thought about the power of the speakers in watts - what this parameter is and how it affects the volume of the equipment.
Today I will tell you how sound in speakers is measured, what volume depends on, and how to find out sufficient parameters for a room of a certain size.
Effect of total output power on volume
Oddly enough, the high power of the equipment does not always mean that it will play loudly and “meaty”. When choosing speakers for your computer, you should remember that watts, roughly speaking, is the amount of energy consumed by the equipment.
Depending on the efficiency of the system (and it can sometimes be extremely low), the final volume can be significantly adjusted.
Sound volume is a subjective characteristic. It is measured by intensity, which is proportional to the square of the sound pressure amplitude. It is affected by the sensitivity of the human ear.
Different people may perceive the same frequency ranges differently. In addition, sensitivity decreases with age.
Total power output is not the only parameter that affects sound pressure. The volume of the system as a whole also depends on the sensitivity of the speakers and the power of the amplifier.
The lower the sensitivity of the speaker, the more powerful the amplifier will be required to activate it.
What does power mean when choosing acoustics?
Thus, the power of an acoustic system is a technical parameter, the value of which is not directly related to the loudness of the acoustics, although it is somewhat related to it. The rated power values of the dynamic heads, amplifier path, and speaker system may be different.
Interesting materials:
Why doesn't the Wifi light on the router light up? Why doesn't the wps light on the router light up? Why does the TP link on the router glow orange? Why is the WAN light on the router red? Why don't the lights on the router light up? Why does the Wi-Fi button on the router not light up? Why doesn't the WLAN light on the router light up? Why is the LAN light on the router not on? Why is there no Wifi from the router? Why can't the router see it?
Measuring systems
Despite the above, the most effective tool for marketers when selling PC speakers remains power, expressed in watts.
Until recently, about 20 years ago, only old acoustics produced by Soviet industry and Chinese equipment, which was beginning to capture world markets, were available on the market.
High-quality European and American electronics were simply not supplied to us due to the sky-high cost, inaccessible to the vast majority of customers.
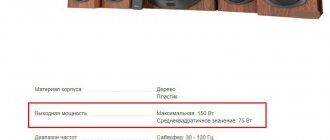
The passport of Soviet, and subsequently Russian electronics, indicated the rated power, which continues to be considered one of the most objective parameters. This characteristic is determined at the middle position of the volume control.
The Chinese have traditionally indicated PMPO - the maximum power that a speaker can theoretically withstand without mechanical damage, and the amplifier can “pass” through itself without burning out or melting the filling.
It was not uncommon to see a proud 500 Watt sticker on a miniature speaker. Naturally, not a single such system was equipped with a power supply capable of accumulating such an amount of energy.
This calculation system was called “Chinese watts”. According to the results of numerous tests, this figure was 20-30 times higher than the rated power. At the moment, fortunately, PMPO is almost never used, and the characteristics of Chinese electronics indicate the rated power.
This is understandable: apart from China and some other Asian countries, today almost no one produces equipment. It no longer makes sense to fight for the market with the help of such cunning manipulations - it has long been captured and monopolized.
Speaker characteristics explained!
It's important to note that these specifications apply to speakers and don't fully apply to soundbars. If you are interested in knowing about these characteristics of soundbars, you can read about it here.
Speaker sensitivity
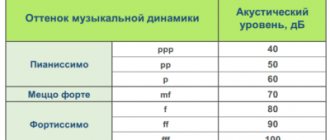
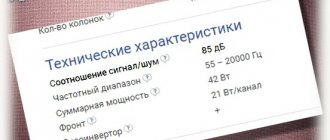
A speaker's sensitivity is a measure of how efficiently it produces volume from the power it consumes. You will measure power in watts and volume in dB or decibels. Sometimes in speakers this is stated as SNR or signal to noise ratio. You can also find it listed by SPL (sound pressure level), dB and dBA.
To determine the sensitivity of the speaker, measure the volume of the speaker at a distance of 1 meter with a power of 1 W. So, if you stand one meter away from a speaker and input 1 watt of power from your amplifier and the result is 85 dB of sound, then the speaker's sensitivity is 85 dB.
Doubling the power supplied to the speaker will increase the volume by about 3 dB. In this case, 2 W power gives 88 dB, 4 W power gives 91 dB, and so on. At 10 watts you produce about 96 dB of volume. That's about as loud as a jackhammer from 50 feet away.
The table below is a useful tool for calculating volume based on speakers with sensitivity ratings of 85 dB and 90 dB. Be sure to measure these decibels 1 meter away from the speaker. You'll lose about 6dB of sound every time you double the distance between you and the speaker.
WATTS TO DB CONVERSION FOR 85 DB AND 90 DB SENSITIVITY RATINGS.
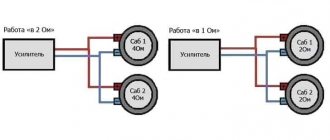
Impedance, resistance or ohms
These three terms are largely interchangeable and are used to measure a speaker's ability to restrict the flow of electrical current. Speakers are typically rated at 4, 8, or 16 ohms. Impedance for speakers is called "nominal impedance" because the actual impedance varies depending on the frequencies of the sound you are currently playing.
A good way to think about power and resistance is to think of it like a garden hose. The resistance is similar to sticking your thumb into a hose while water is flowing. Voltage is the pressure in the hose, flow is the current, or how much water passes through it, and ohms is the resistance, or how much of the hole is covered by your finger. Basic formula: current = voltage / impedance.
The most important thing to remember is that the lower the resistance, the more current will flow. If you have a speaker output marked "4 ohm minimum", you can connect one 4 ohm speaker or two 8 ohm speakers to that output. If you connect two 4 ohm speakers to this output, it will overload the amplifier and probably destroy it.
Powered by audio/video receiver or amplifier
The wattage ratings advertised by the manufacturer of an A/V receiver or amplifier can be confusing and misleading (which is why we wrote the guide). This can be total output power, output power per channel, or output power when using two channels. For our purposes, we will use the "power per channel" measurement or WPC measurement.
However, an amplifier's WPC is a measure of how much power an amplifier can deliver to each channel of its system. Like speaker sensitivity, loudspeaker amplifiers can produce non-linear power depending on the speaker's power. You might think that a 20-watt amp would produce twice the volume of a 10-watt amp, but that's not the case. To double the output volume of a 10-watt amplifier, you will need a 100-watt amplifier. It takes 10 times more energy to double the volume.
Calculation of amplifier power requirements
Remember that formula we discussed earlier? A speaker with an 85 dB SPL rating will produce 85 dB of sound to a person 1 meter away at 1 Watt. If this were the rating for your 75 watt speaker, then that means that person would experience about 104 dB and your speaker would receive 75 watts of power.
104 dB is the maximum volume that is enjoyable for most people. So this is great! Why do you need more? The answer is simple: it is at a distance of 1 meter. In the absence of other interference, the sound decreases by about 6 dB every time you double the distance. So at a distance of two meters 104 dB becomes 98 dB, and at a distance of 4 meters it becomes 92 dB. At 8 meters, that 104 dB becomes 86 dB, which is roughly the volume you hear in a movie theater.
86dB is still pretty loud, but as you can see, filling a large room with a lot of sound can quickly become a problem, especially since the above scenario uses the maximum power your speaker can handle.
In this article you can get an even more detailed overview of the amplifier's characteristics
Cabinet size
The size of the speaker cabinet (also called the enclosure) can have its own impact on sound quality. This doesn't mean that larger size automatically means better sound. Larger speaker systems may have different drivers, components, and high-quality materials. It is also possible to create a large speaker with cheap components and poor sound quality.
Companies need to consider thousands of factors when designing a speaker. Installing drivers and other speaker components inside a cabinet can automatically create its own set of problems. The engineer's job is to ensure that the speaker's components work in tandem with the enclosure they are housed in to create the best possible speaker.
However, there are some unusual speaker designs that have no cabinets at all and are quite expensive. These speakers are called "electrostatic speakers" and can cost tens of thousands of dollars. At the very least, they are evidence that with good engineering it is possible to eliminate the speaker enclosure entirely.
So how does cabinet size affect sound quality? As a general rule, a larger speaker will likely sound better because there is more room for materials. It will be better designed and weigh more, which will reduce any unwanted vibrations while using the speaker.
With that said, bigger doesn't necessarily mean better. A well-designed speaker can be smaller but produce much better results than a larger speaker, but that smaller speaker will likely cost significantly more. Check out our other article for more information on speaker quality by size.
Can too much power damage the speakers?
Too much power can damage your speakers. Connecting a 100-watt amplifier to 75-watt speakers will not cause any problems. In fact, under most normal listening conditions, connecting a 100-watt amplifier to a 75-watt speaker is perfectly fine. The problem occurs when you turn up the volume so much that your amplifier is delivering more than 75 watts to the speaker.
It's likely that you'll start experiencing severe distortion long before speaker damage actually occurs. However, once your amplifier starts sending more power than the speaker can handle, it will damage the speaker and damage the components.
On the other hand, if you are using a low power amp and turn the volume all the way up, you are actually sending voltage directly to the speaker. This will quickly burn out the driver and ruin the speaker. Many people think that the speaker can't handle the volume, but that's not true. This is actually due to the fact that the amplifier itself cannot process the signal it is trying to send and sends. It is a processed electrical signal instead.
Can speakers draw too much power from an amplifier?
Speakers can draw too much power from the amplifier and damage components inside the amplifier. This is not because the speaker is drawing too much power, but because there are too many speakers or because the impedance of the speakers is too low.
If you use a speaker with an impedance rating lower than the output jack it is connected to, then the speaker it is connected to will have trouble delivering the correct current. If we go back to our garden hose analogy, it is almost as if the water in the hose accumulates so much that it starts to leak.
You might also think that the simple solution to all of this would be to simply add more speakers. Unfortunately, if you splice speaker wires together to install additional speakers in your amplifier, each speaker will draw the same amount of power from the amplifier.
Let's say you have a 50 watt amp and the volume is loud enough to use 20 watts. You then connect the speaker wires together to add an additional speaker to that channel. Each of these speakers consumes 20 watts of power. Now, if you connect a third speaker to this output jack, you will require 60 watts of power from a 50 watt amplifier.
Remember how we talked about doubling the power to add 3 decibels of sound? This is exactly what happens when you add additional speakers. You may be trying to double the volume of your system. Unfortunately, adding another speaker, like increasing the power, will only add 3 dB to the volume.
This is a completely new way to ruin the entire home theater system. You may damage your amplifier and speakers if you connect the system this way at too high a volume.
So how do I calculate the power I need?
The first thing you should pay attention to is the sound pressure level of the speakers themselves. Let's take this model as an example, which has an SPL of 88. We'll call it the S. Next, we'll look at the actual room in which we'll be installing our entertainment center.
We'll be aiming for a maximum decibel rating of 102 dB, which is higher than most people would like. To get 102 dB at 1 meter, we start with 88 dB at 1 watt and add 3 dB every time we double the power. If we go back to the previous table, we see that we need 16 watts to reach 102 dB.
However, if you go back another meter, you will lose 6 dB. You will then need to double the power two more times to compensate. This would mean we would need a 64 watt stereo system. Since 64-watt stereo systems don't exist, you'll need a 75- or 100-watt-per-channel amplifier.
If you plan to use surround sound, you also need to consider each speaker. If we assume that all speakers are the same, then each speaker will produce 3 dB more sound. In this scenario, you could, for under $1,000, pair that 80-watt Denon amp with those 130-watt Onkyo speakers.
Other standards
In this topic one cannot fail to mention the DIN 45500 standard, which first classified the concept of Hi-Fi equipment.
According to accepted standards, DIN Power is measured here by applying a signal with a frequency of 1 kHz to the linear input for 10 minutes.
When 1% THD is reached, power is measured. This system is completely identical to the Japanese EIAJ. DIN Music Power is another parameter, the maximum signal that the equipment will withstand without damage for a long time.
This indicator meets IEC Power, according to the International Electrotechnical Committee standard IEC 268-5. The duration of the load is 100 hours.
RMS is the maximum sinusoidal power, that is, the one with which the device can operate for an hour without damage. Typically this value is 150-200% more than the Soviet rated power and 20-25% more than DIN Music Power. AES2-1984 is close to this standard, according to which measurements are taken over a two-hour period.
How to improve TV sound quality
1. Soundbar - soundbar.
2. Stereo system, possible with a subwoofer.
3. Acoustic multi-channel systems in 5.1 or 7.1 formats.
4. High-quality wireless headphones.
Super acoustics for recreation centers
If after the purchase the only money left is to wash the TV, then you can assemble a speaker amplifier with your own hands. On our website there is a huge number of ULF circuits with detailed descriptions, and if you still have questions, the forum will help you. The cost will be only a couple of dollars to purchase an UMZCH microcircuit, and probably everyone has passive speakers.
As a budget option, I recommend purchasing regular computer active speakers. For example, FD-244 copes with this task perfectly. Their price is 40e.
Ideally, you can buy a receiver. Even budget-level devices, up to $300, produce powerful, clear sound that can easily drive a 200-watt speaker.
Let's sum it up
1. Not a single, even the most expensive modern TV can compare in sound to Soviet TVs in a wooden case.
2. When planning to purchase an LED 3D TV, immediately budget a hundred or two dollars for the purchase of external acoustics.
3. Give preference to voluminous and heavy speakers with large diameter speaker cones.
And finally . The LG 47″ TV, bought 4 months ago for 1200, has already begun to noticeably wheeze even at a low volume level. The built-in speakers turned out to be downright ugly.
Discuss the article THE SOUND OF MODERN TVS
A simple pulse metal detector for beginner radio amateurs - “PIRAT”. Development by our forum team.
Design power (definition)
One of the main stages in the design of power supply systems for a facility is the correct determination of the expected (calculated) electrical loads of both individual electric power supply units and load nodes at all levels of the power supply system.
Load design values are loads corresponding to such a constant current load (
), which is equivalent to the actual time-varying load for the greatest thermal impact (without exceeding permissible values) on the element of the power supply system.
There are various methods for determining design electrical loads, which in turn are divided into main ones; and auxiliary.
The calculated electrical loads include the calculated values of active power (
), reactive power (
), full power (
) and current (
).
Taking into account the type of load
Household electrical appliances are characterized by two types of load:
- Active;
- Reactive.
The active (ohmic) load is consumed by devices that convert the received energy into heat. This is an electric stove, iron, hair dryer, air heaters, etc. The reactive load is consumed by other electrical appliances, which convert only a small portion of the energy into heat. The bulk of the energy consumed is used for another purpose. Examples of such appliances include a refrigerator, vacuum cleaner, TV, computer, etc.
If you need help choosing the generator power for your home, industrial workshop or any other facility, contact our specialists for qualified advice.
Example
Let's say we have a generator with a power rating of 3 kVA and cos φ equal to 0.8.
In this case, the rated power of this installation will be equal to: 3 kVA x 0.8 = 2.4 (kW)
Now you can understand why power can be indicated in certain units of measurement, in watts (W) or Volt Amperes (VA). Some manufacturers, in order to save the consumer from the need to carry out calculations, simply indicate in the accompanying documentation both power values - nominal and maximum. There are also options when the manufacturer indicates only one of the capacities and gives the value of the power factor. Some unscrupulous companies may hide the power factor from the consumer. This is done in order to pass off the generator as a more powerful unit than it actually is.