It is a mistake to believe that purchasing high-quality speakers and an audio system automatically guarantees excellent sound. To set the right sound, there is an equalizer program. In Windows OS, the equalizer is located in the sound settings; for more accurate work, you can download the program from the Internet. What is an equalizer?
An equalizer is a special device or program that allows you to adjust the timbre of an audio signal and sound quality. The adjustment occurs by changing the amplitude of the audio signal frequencies. Simply put, it is a program that allows you to increase and decrease the volume of different areas of the range. The equalizer allows you to obtain different sound timbres during processing.
Graphic equalizer
This type is one of the most common equalizers. It consists of several sliders that add or reduce different frequency ranges. A graphic equalizer is characterized by a fixed frequency band.
The advantage of such an equalizer is its ease of influence on a certain spectrum. It provides the ability to change different parts of the spectrum simultaneously up and down.
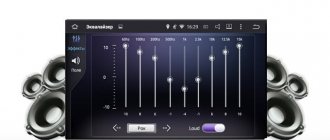
The simplest graphic type option is a three-band equalizer. In this form, it is possible to adjust the low, high and mid frequencies. This is the most primitive example. The more bands an equalizer has, the more flexible the settings become. A PC program often includes 5 bands, which allows you to work with audio material without being overloaded with unnecessary functions.
Windows Media Player
The equalizer for Windows can be found in two places: in Windows Media Player and directly in the Sound settings. Now we will talk about the first option.
By installing an equalizer for Windows in Media Player, you can only influence the playback of music files in this player. That is, if you run the same file in another player, the sound will be the same as before the changes.
So, you have turned on music or video, then right-click and select “Additional features” from the menu. Next in the list, click on “Graphic Equalizer”. For Windows 7, this instruction works one hundred percent.
That’s basically it, the equalizer is open before your eyes on the monitor. You can change the position of the sliders and notice the difference in sound, and you can also select a Preset, but more on that later. There is no point in telling now how to set up the equalizer for Windows, since it is the same in all operating systems. Therefore, now we will talk about how to open it in each of them, and at the end we will analyze in detail how to configure it.
Parametric equalizer
A parametric equalizer is practically not found in standard PC programs, but if necessary, it can be easily downloaded on the Internet. For a complete understanding, it is better to download it in Russian. The parametric equalizer allows you to adjust the width of the bands.
In this type of equalizer, a separate band has the ability to set parameters, such as: center frequency, band width, amount of lift and roll. Sometimes a parametric equalizer allows you to change the filter type for each individual band.
A parametric equalizer allows you to select the required frequency and adjust it with the greatest accuracy.
Definition
Tone block, EQ, equalizer - it's all the same thing. The definition is as follows: it is a program or device designed to raise or lower the volume of various areas of the audio frequency range. An equalizer is capable of equalizing the entire amplitude of frequencies and the characteristics of the signal itself as a whole. It is important to know that this program or device only works with the audio signal and adjusts it selectively, depending on the selected frequency.
This definition is complex and it is difficult for the average user to understand the whole essence, so now - in simple words. An equalizer is a program (in this case) that works with individual sound frequencies. As you know, there are low frequencies and high frequencies. Low is bass, high is falsetto, or as it is also called, squeak. So, the equalizer can lower or increase the volume of these areas. But sound can be divided not only into two frequencies, it can be divided into n frequencies. Likewise, the equalizer has several bands; the eight-band version is more common.
Most often, this program is used in the audio industry, but now let’s talk about how it can help the average person.
Cutting equalizer
The name of this type is directly related to how the equalizer works. A cut equalizer allows you to cut high and low frequencies, hence the name. A filter set to low frequencies will cut off only low frequencies, leaving high frequencies alone.
Low-frequency cutting is most useful when it is necessary to neutralize low-frequency noise: train noise, passing cars and other street sounds.
High frequency cutting is used to combat the noise of musical instruments.
Third party programs
It is also possible to download an equalizer for PC. For example, there is a program called NeonVisual. By installing it, you can make flexible adjustments to all frequencies, thereby improving the sound of your speakers.
In addition, the program offers a user-friendly interface. Even an inexperienced user will be able to figure out all the intricacies on their own.
In principle, there are an unimaginable variety of such programs, but it is pointless to talk about each of them. They are all similar, and if you know how to use them, there will be no problems.
Well, in the meantime, let's move from the Windows operating system to Linux.
What is an equalizer on a phone?
equalizer, from equalization - to equalize) is a device or program that is used to adjust the balance of sound frequencies. For this equalizer
allows you to increase or decrease the sound volume in certain frequency ranges.
Interesting materials:
What should you say before going to bed to make your betrothed dream? What should I enter in the zip code? What do you need to know to become an accountant? What do you need to know to become a programmer? What do you need to know to become a dentist? What do you need to know to study calculus? What does a programmer need to know in mathematics? What does a new game designer need to know? What does a neurologist need to know? What does an appraiser need to know?
Equalizer and headphones: why is it needed?
It would seem that if there is no room, and the music comes directly to your ears (from the ear pads of the headphones), what then to compensate?
1. At a minimum, the musical composition itself. It is difficult to assume that the original recording (master) was performed poorly. But the copy you received for listening may have any flaws.
2. Your ear for music. We are not talking about abilities that are developed in music school. Each person perceives the sound of voices and musical instruments differently. The equalizer allows you to adjust the “orchestra” to the listener’s taste.
3. Your preferences at a particular moment of listening. For example, sitting with headphones on, you wanted to be in a concert hall or stadium. Equalizer settings will help create a sense of presence.
Any software equalizer has a list of average presets. You can go through them by pressing the corresponding button on the control panel, and remember several suitable options. This mainly concerns types of musical compositions: classical, rock, disco, etc.
Some advanced programs have preset settings for different listening conditions: room, concert hall, open space. Of course, when using headphones we are talking about simulating the effect of presence.
Corrective equalization: attenuation of frequencies with an equalizer
Corrective equalization corrects signal problems such as buzzing, unpleasant resonance, and frequency collision. To make adjustments, sound engineers cut certain ranges, which hides or completely eliminates problems in the signal. It is better to use frequency cutting before boosting other sounds - this way you will minimize the appearance of new problems when boosting frequencies.
To understand what needs to be cut from the signal, listen to the instrument part and evaluate its sound. Determine by ear what is too much in the sound - this will make it easier for you to decide which frequencies to process (for greater accuracy when processing, you should be guided by the frequency table of musical instruments). Some equalizers, such as the one built into iZotope Neutron, are equipped with an analyzer that automatically places points on the spectrum, recommending frequencies for processing - this function will be a good help for novice sound engineers who are just learning to use an equalizer.
When working with equalizer, rely only on your ears, since it is easier to hear problems in the mix than to immediately find the frequency ranges that cause these problems.
If you're hearing muddy mids or sibilant vocals, you can find a frequency range to cut by turning up the gain as much as possible, using the Q knob to narrow the width of the EQ curve as much as possible, and start moving the point across the spectrum. Such a hypertrophied boost will make it easier to find problem frequencies: you need to correct the signal where the previously identified shortcoming of the mix/signal is especially pronounced. How much to attenuate the signal is up to you, since everything here depends on what kind of sound you want to get.
Frequency Isolation in iZotope Neutron
Boosting works better on static elements in a mix than on dynamic ones. One processing point is enough to eliminate the low-frequency hum of the kick drum, which sounds almost unchanged. When working with the same vocals, which can change greatly in different parts of the song, one processing point will not do - a more comprehensive approach will be required. Be prepared that as you move the amplified point across the spectrum, there will be several frequency ranges in the signal that need to be adjusted.
The more active and varied the signal itself, the more frequency edits it will require to fit into the mix.
When working with an intense signal, it is better to set up automation in the EQ plugin or use a dynamic equalizer. The latter will help adjust the operation of the equalizer so that it adapts to signal changes. Some equalizers (such as the one included in iZotope Nectar) are equipped with a Follow EQ function, which takes into account changes in the signal and adapts to them.
ATTENTION!
With corrective equalization, the frequencies of a narrow or particularly narrow Q curve are pinched. It must be remembered that too narrow amplification of the signal makes the sound unnatural and unpleasant.
Second way
The second option would be to download a more functional audio player, such as TuneShel or Radsone. Already in their settings you can use an equalizer with many bands.
So, if anyone does not know how to download and install these applications on their phone, then detailed instructions will now be given.
- Find the App Store application on your phone and launch it.
- Next, at the top of the screen, click on the “Search” section.
- In the field to fill out, write the name of the program you need and click “Search”.
- Now the application you were looking for should appear in front of you. If this does not happen, check whether you entered the name correctly.
- Click “Download” next to the application image.
- Wait for the download and installation to complete, after which you can use it.
As you can see, downloading another audio player is not difficult.
Formative equalization: boosting frequencies with an equalizer
After the signal sound has been corrected, you need to look at what is missing from the sound of the instruments and the overall frequency picture of the mix. Formative equalization, aimed at enhancing the frequencies in the signal, will help solve the lack of certain frequencies. When boosting frequencies, you need to rely on wide, but neat and smooth curves that will enhance and improve the entire frequency range.
The difficulty with boost largely lies in the fact that there is no single recipe or universal advice on how much to boost frequencies. Over-boosting the kick will make it sound boomy and rumbly, while under-boosting will turn the kick into something like a leaky boot, cowardly squelching through the puddles at the back of the mix. Boosting frequencies in the lower middle region (150-350 Hz) will make the signal warmer and richer, but only if the boost is exactly as much as needed - excess amplification creates an unpleasant muddiness and blurriness of the signal.
Tonally balanced mix
If you doubt the correctness of the decisions made and are not sure that the changes made improve the sound, use analyzers like the Tonal Balance Control module included in the iZotope plugins. By placing the tonal balance module on the master channel, you will see a frequency map of the mix, which can be compared in real time with a reference track. This way you'll see what the mix is missing compared to a high-quality commercial recording, and you'll also understand what edits need to be made.
iZotope Neutron/Nectar will show you which instruments and signals require editing if you move the mouse in the interface while holding down the Alt/Opt key. In addition, the company’s plugins have a built-in intelligent Track Assistant, which analyzes the signal and offers presets that improve the sound of the mix. The algorithm is far from ideal and its choice should not be trusted. However, as a starting point for beginning mixing, his tips and advice are quite helpful.