Electrician in the house
Encyclopedia about electricity from A to Z
Masters catalog
Find the best master or company in your city
Good speaker wires are the key to clear sound
When purchasing good acoustics, an inexperienced person never thinks about the fact that for high-quality sound of the entire system, in addition to the speakers, it is necessary to acquire the appropriate wires. This is especially true for models in the mid-price segment, where the manufacturer can equip the product with good speakers, and at the same time save on sound-conducting cables, or not include them at all.
The wire for speaker systems is as important a detail as the amplifier, which, by the way, performs the main job in the entire system.
- Main characteristics of wires What is a “bottleneck”
- Characteristics of speaker wires
- Wire resistance
- Other factors
- Types of Speaker Wires
Main characteristics of wires
To help you better understand the essence of the whole problem, let's dive a little into the theory and see how the sound system functions. The above diagram is relevant both for expensive Hi-Fi acoustics and for ordinary speakers on a personal computer.
What is a bottleneck?
The term “Bottleneck” or “Bottleneck” can often be heard among computer geeks and people who review PC hardware. It is used to designate an element of the system that inhibits the remaining parts, that is, the weakest link.
The overall performance of the system will always be equal to the power of this particular element, despite the presence of higher-quality circuit parts.
A symbolic representation of how low-quality components slow down the entire system
This principle applies not only to computer peripherals, but also to any electronic circuit, and even mechanisms.
So, what are the dangers of using low-quality wires? Let's take a quick look at the operating principle of a simple transistor amplifier.
Circuit with a transistor without specifying other elements of the circuit
So:
- The diagram above shows a simplified diagram of the operation of a single-transistor audio amplifier. We did not indicate the remaining elements, so as not to complicate the process of understanding the functioning of the device, and limited ourselves only to the transistor itself.
- A transistor is a semiconductor part of any modern electronic device. It was thanks to him that the equipment was able to decrease in size and seriously lose weight.
- It has three terminals called: base, collector and emitter.
- The current through the transistor flows between the collector and emitter in one direction (varies depending on the type of radio component). The base serves as a key to control the flow. The principle is simple: the key is closed - no current flows, open - there are no restrictions.
- But the base has not only two positions: “on” and “off”. The “door” opens slightly, depending on the voltage supplied to the base (from 0 to 1 V). This is the principle of operation of the amplifier.
- The voltage at the emitter is several times higher than the base voltage, for example, 10V versus 1V. The ratio of these quantities is the gain. The base is supplied with an alternating signal from a player or microphone, which constantly changes its value. At this time, the transistor repeats the signal, but at higher voltages, which, in turn, is supplied to the speakers.
Let's assume that our amplifier can magnify the signal 10 times and produce a clean signal in the frequency range from 20 Hz to 2 kHz - this is the range accessible to human hearing. But to connect to the speaker, we will take a low-quality speaker wire.
As a result, due to the fact that the wire is not able to transmit all frequencies, we get deformed sound with noise, or a decrease in the power of the conducted signal, part of which is spent on heating the wire. All the advantage of our good amplifier is reduced to nothing. That is, in the end you will get the following circuit: signal - amplifier - “attenuator” - sound. Doesn't anything about it bother you?
Characteristics of speaker wires
Let's identify all the characteristics of the conductor that affect the quality of the transmitted signal.
Connecting the speaker system
The sound quality directly depends on the following technical characteristics of the wire design:
- Type of conductive core material;
- Properties and characteristics of insulation;
- Feature of the internal structure of the cable.
The quality of the metal used affects the purity and depth of low frequencies (bass). The accuracy of timbre and sound transmission depends on other characteristics.
Two-piece speaker cable
Today, the most affordable metal with high conductivity characteristics for acoustics is copper. It is used in the manufacture of the vast majority of cables. But copper comes in different qualities, with different impurities that affect its properties.
As a result, copper wires are divided into the following types:
- TPC is copper obtained using rough cleaning technology. Wires made from this material are used in budget acoustics, where the requirements for sound quality are low.
- OFC is oxygen-free copper with good conductivity. This conductor ensures signal transmission with virtually no loss, and is used in systems in the mid-price segment. Due to their reasonable cost and characteristics, these wires are most widely used throughout the world.
- RSOSS – wires made of pure copper obtained by continuous melt drawing. This technology was developed by Chinese engineers and is successfully used to manufacture the highest quality products. But you should not think that this applies to Chinese products.
Advice! Some companies create their own wires by changing or improving these technologies. For example, it produces an exclusive product with an enlarged crystal lattice, which is labeled as LC - OFC.
Silver acoustic wire
As you know, precious metals conduct current much better than copper. But, if the price of gold and platinum is completely incompatible with such use, then silver is used quite often in the manufacture of wires.
So, the price for 1 meter of pure silver wire is 100 euros, and this is far from the limit. These products are used in conjunction with elite equipment and expensive concert equipment.
Much more often, you can find so-called composite wires, consisting of several metals. For example, copper wires are coated (tinned) with a thin layer of silver or tin, which gives these wires enhanced properties.
Component speaker wires "Morel"
Copper is combined not only with metals, but also with carbon conductors. Such additives give the conductor certain properties. Such wires are called component wires.
Advice! If your wire is not marked in any way and is made of unknown alloys, then feel free to throw it in the trash and run to the store for a new one.
Wire resistance
So, after reading, let’s summarize - the main value for an acoustic cable is its throughput, which is directly affected by the resistance of the conductive part. The higher it is, the worse the signal travels through the wire.
As you probably already guessed, each type of alloy is distinguished by this indicator. But the resistance of the wire depends not only on this. The length and cross-section of the cable are of great importance.
Resistor - radio component to reduce voltage and current
What does the concept of “resistance” mean in an electrical circuit? Resistance is the ability of a material to resist the movement of electrons. The higher it is, the lower the throughput of the conductor (in electronics, special elements called resistors are used to reduce the current).
Let's make a small analogy with a water supply:
- Let's imagine that we have a pipe through which water flows at a speed of 2000 liters per hour. Its diameter corresponds to the amount of fluid passed through.
- But what happens if we cut a section of another, smaller pipe in the middle, or slightly cover the tap?
- That's right. The amount of water passed through will decrease, since an additional obstacle has appeared on its path, impeding the flow - that is, resistance is created.
- Or the opposite situation - we increase the diameter of the pipe at the same pressure as before. We immediately draw the following rule: reducing resistance without increasing the load does not affect the performance of the system.
- The situation is similar with electric current - the thinner or longer the wire, the higher its resistance. A thick cable will transmit the signal much better, but looking at the rule described above, let us clarify that its diameter must be selected to match the peak signal power.
Attention! Acoustic wire 2x4 mm², capable of transmitting a signal almost at the speed of light (98% excellent result).
Wire Resistance Table
Calculating wire resistance is very simple. Use the table below for this. For example, the diameter of a 10-meter copper wire is 1 mm. The resistance of 1 meter of this wire is 0.023 Ohm, which is very small. All you have to do is multiply this value by the total length of the conductor: 0.023*10=0.23 Ohm.
Next, open the instructions for your amplifier, and look at the optimal value recommended by the manufacturer. If necessary, you can carry out the calculation yourself, but we will omit this part, since we had no intention of diving into formulas from the very beginning.
Let's go back to our plumbing for a moment. What happens if the pressure in the pipe is too high?
That's right, it will vibrate, and perhaps even burst in the worst place. In electronics, this phenomenon is called a short circuit (short circuit). Of course, it does not threaten you when connecting acoustics, but loss of signal, deterioration in sound quality, and heating of wires are quite common phenomena.
Other factors
Speaker wires in different insulation
Let's move on. The next factor influencing the quality of wires is the insulation material, which also contains a certain set of characteristics.
We will not go deeper into these jungles, and we will only note the main thing:
- The best insulation is considered to be Teflon, especially foam, or low density.
- Next in descending order is polypropylene - wires with such insulation are slightly worse, but have a more reasonable price.
- The most common insulating material today is polyvinyl chloride. But such acoustic wires, due to the effect of charge accumulation by the dielectric, greatly distort the sound, and are clearly not suitable for high-quality sound systems.
Advice! Good insulation of the acoustic wire must be elastic, otherwise, if there are strong bends, it may be damaged.
An additional advantage of high-quality wire is the presence of a screen that will prevent the appearance of noise. This type of cable is recommended for car audio and expensive Hi-Fi speakers.
Double insulated and braided shielded speaker cable
USB audio cable test
I know it's useless, but just in case. to understand: “The concept of “digital stream” for audio, where digital-to-analog conversion is used, consists of two independent parts:
— information component (zeros and ones)
— base clock frequency and its processing when fed into the DAC circuit. In fact, these are two completely independent parts of digital data transmission. The difference in the setting and processing of the clock frequency affects the sound. Therefore, in the audio world you cannot limit yourself to only the first part when comparing digital streams. We also need to take into account how the clock frequency is set. And then it turns out that two devices produce DIFFERENT streams. And it sounds different, which is logical.
But at the same time, in the computer and telecommunications world, due to the technological solutions and interfaces used, there are simply no problems with clock speed. Why isn't this used in audio? Don't know. They just probably don’t know how to work with such an elemental base. Well, just think about it, the system bus of a computer processor operates at a clock frequency of gigahertz! and not a SINGLE BIT is lost. Well, I’m not talking about transatlantic Internet transmission cables at all. Do you really think that it uses real-time clock synchronization at the ends of the cable? Yes, this is simply impossible at such distances. You don’t have to worry about synchronizing clock frequencies; it’s enough to just do asynchronous data transfer to the DAC chip itself. It's just different chips and knowledge that the audio world lacks. Look at the development of USB interfaces for music. There they followed exactly this path and immediately received an increase in quality. And now nothing depends on the cable when working via USB in asynchronous mode. The main thing is that he misses 192/24 without losses. And no shamanism.
True, after this it will no longer be possible to make money on expensive digital cables, a CD drive and other audiophile bells and whistles. I apologize if I offended anyone by accident." (c)
On a personal note: in fact, the influence of a USB cable during asynchronous transmission is the cost of the influence of parasitic interference on the very process of digital-to-analog conversion to a DAC, namely on the base frequency (clock), since the sensitivity of hearing to its change is very high. But in any case, asynchronous USB transmission plus a competent noise-proof design almost completely neutralizes the influence of the USB cable.
PS SPDIF (AES, Toslink) is a pseudo-synchronous interface with a noticeable influence of “digital” cables on the sound.
“In fact, such an unsuccessful method of transmitting a synchronous stream as SPDIF with master clock restoration on the receiving side is strongly influenced by many factors. It is on the process itself and the result of restoring the clock signal. The magnitude and spectrum of jitter, and, accordingly, the nature of the sound depend on the quality of the line driver, on the level, nature and spectrum of interference induced on the cable, on the properties of the master clock restoration PLL system in the receiver.” (c)
Wiring structure, standard inputs and connections
In this part of the article we will look at the structure of wires and get acquainted with the list of terminals and connections for them.
Types of Speaker Wires
Acoustic wires can be single- or multi-core. The latter, in turn, are divided into three types.
Bundle-shaped conductor: The arrangement of current-carrying conductors in such a cable is uneven, which makes it vulnerable to reflected signals. Therefore, using this type with acoustics is not recommended.
Concentric speaker cable
The next type of wire is called concentric. Due to the fact that the conductors are arranged evenly, an almost ideal circular cross-section is formed along the entire length of the conductor, which gives stable resistance in all areas, and as a result, signal transmission with low losses.
Stranded twisted wire
The best design is the rope one. In essence, this is an improved model of the previous cable, but with better flexibility of the wire itself, which is very important when laying in areas with sharp bends.
Single-core wires have the highest throughput, but due to their high rigidity, their use in compact systems is quite problematic.
Twisted pair speaker cable
Twisted pair cables stand out, as they have many interweaving options. Some of them are equipped with complex shielding, which significantly affects the quality of the transmitted signal.
In these wire models, both monolithic and multi-core current-carrying conductors can be used. The farther they are spaced from each other, the clearer and more detailed the frequencies from the amplifier are transmitted - but at the same time, the cohesion of the sound begins to suffer. Therefore, the most optimal combination of these parameters is the main task of the engineers creating these wires.
Speaker wire 2x4 mm: twisted pair
Twisted pair comes in the following models:
- UTP – standard cable without screen;
- FTP – this model of speaker cable has a foil screen to reflect interference;
- STP - each wire core has its own screen, plus a common screen is added in the form of a braid of copper wire;
- S/FTP – the external shield for the cable is a twisted copper pair, each of which has a foil braid;
- SF/UTP - twisted pair has no protection, but the screen of such a wire consists of both foil and wire.
Advice! Even well-shielded wires with a double layer of insulation can pick up extraneous noise, so when laying them on metal structures (car interior), it is recommended to first place them in corrugation.
What do the tests say?
Testing speaker wires
Each type of cable has already been tested by someone many times, so users have formed their own opinion about each model in particular.
So, what do professionals on the Internet advise:
- Naturally, wires made of pure silver have the best performance, which can provide sound transmission with overtones and original sound recording, without any distortion.
- Wires made of monocrystalline copper (MCC) are an excellent solution for all types of frequencies. Speaker wire for a subwoofer made of this material will provide clean, deep bass.
- When choosing oxygen-free copper cable, you are faced with a real problem. The reason is that the sound quality on wires from different manufacturers varies greatly. This is especially true for Chinese products, most of which do not stand up to criticism.
- Composite wires are also quite good, but sometimes tin-plated copper can create a lisping effect. Silver-plated models give the sound more brightness, which is rather considered a plus.
Advice! When choosing a wire, avoid unmarked options. It's better to buy a well-known brand. For example, products from the budget segment are highlighted.
Terminals and connectors
We think that it is no secret to anyone that the type of terminal is selected depending on the shape of the mating socket with which the amplifiers and speakers are equipped. But we still think that going over the main ones will be very useful.
U-shaped terminals
The photo above shows a U-shaped terminal, which is most often used when installing car amplifiers. The connection has an insulating casing for protection, but still, it is recommended to additionally wrap the joints of the insulators with electrical tape. This is done because the contacts in the system are very close to each other, and vibration of the car body can expose the insulation.
Subwoofer terminal block
Screw clamps do not require any additional parts from you. It is enough to insert the end of the wire, stripped of insulation, into the hole and tighten the nut. Most often, such connections can be seen on woofers and home Hi-Fi systems.
Screw terminals
Screw terminals are used when connecting professional equipment, expensive acoustics and mixers for sound recording.
Terminal clamp
Clamp terminal blocks are a very convenient solution used in most computer speaker systems, inexpensive home theaters and music centers. This connection also does not require mating connectors.
Ready solutions
If your sound system is equipped with sockets instead of terminal blocks, then you will have to buy a ready-made speaker cable for them. Although the market most often presents samples of Chinese industry, the quality of which is clearly not the best, you can still find products from well-known manufacturers, since all of the above fully applies to these products.
Computer speaker wire
For example, to connect a separate amplifier or music center to a computer sound card, a 3.5 mm mini-Jack to tulip cable is used. By the way, in radio stores you can always find a variety of adapters and non-standard cables that will allow you to connect non-core devices into the system.
Tulip cable
Many systems, including automotive ones, are equipped with tulip sockets. This connection is very convenient and reliable. Wires of this type can be used for both audio and video transmission.
Connecting speakers
Connecting an audio system with your own hands is very simple. The main thing is to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and follow the connection sequence.
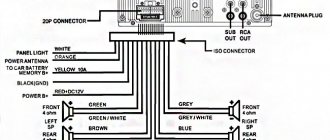
Speaker cable markings
Each amplifier supports a certain number of connected speakers, which you can select yourself according to the required connection diagram. Ready-made systems are equipped from the factory and have the appropriate designation: 2.0; 2.1; 5.1; 7.1 – these numbers indicate the number of speakers in the set.
- The first number indicates how many high- and mid-frequency outputs the amplifier has. The second indicates the presence of a low-frequency subwoofer in the system.
- To avoid confusion, open the attached connection diagram, where you will see the names of all the pins, which, by the way, are duplicated on the amplifier itself and the speakers.
- All you have to do is connect all the elements in series. But be careful not to confuse the polarity. The positive terminals of the amplifier and speakers are usually indicated in red, and the negative terminals are black.
- The positive wire for acoustics is marked with a colored stripe (see photo above), or has red insulation. Minus - may be black, or not have any markings at all.
By connecting the speaker wires to the terminals in series, you guarantee a high-quality result, without the risk of tangling the cables. Believe me, it will take you much more time to unpack the system and arrange it around the room.
That's all - we hope that we were able to present the material as fully as possible. Read more articles on our website!