It's always nice to listen to music or watch a good movie with high-quality sound. Today, the choice of audio systems is simply huge, and it is easy for a person who is poorly versed in such technology to get confused. Find out how to choose speakers for home use based on your preferences. The acoustic system must have not only an attractive appearance, but also optimal parameters for specific purposes.
The Best Hanging Speakers for Home
The main features of the suspended speaker system are a convenient positioning system, space saving and preservation of playback quality. These can be two-lane or multi-lane designs, and the design, characteristics, brand and model are a matter of individual choice. Based on approved reviews and expert assessments, the best suspended models of 2022 were identified.
Show CS-304
Single-ended pendant speaker with impeccable design. Most often, such a column is hung on the wall to save space. Maximum active power 100 W, sound pressure 114 dB, frequency range 180-18000 Hz. The manufacturer offers a loudspeaker in an aluminum case with a mounting element.
Dignity
- Duration;
- Aluminium case.
- Easy installation;
- Slim and elegant body;
- High performance;
Flaws
Heavy weight.
For some, the heavy metal body is a disadvantage of the product. Others, on the contrary, consider this fact a guarantee of long service. This speaker system is used for a computer and home theater.
APart OVO5
This in-wall speaker is designed for use in small to medium sized rooms. The OVO line is full of models with different layouts, speaker sizes, and “fillings”. The OVO5 is a two-way wall-mounted version with high-quality 5.25-inch speakers. Frequency range 70-20000 Hz, power 80 W, maximum pressure 110 dB. The case is made of durable plastic, resistant to mechanical damage. Has a reliable bracket for fastening.
Dignity
- No noise at maximum volume;
- Wide frequency range.
- Compactness, lightness;
- Clean and transparent sound;
- Clear Bass
Flaws
The fragility of plastic.
This is an excellent offering for those looking for clear and transparent playback at any volume. There is no noise, distortion, or vibration in the bass; sensitivity appears only at maximum volume. Two speakers serve a fairly large room.
Material of manufacture - what is it made from?
The material from which the speakers are made affects the sound quality. It can be plastic, wood, chipboard. Each material has its own pros and cons. For example, plastic is a cheap, lightweight material. Even speakers with unusual designs distort the sound at high volumes. Usually, they are connected to a computer.
Their cost is one of the lowest. If you plan to listen to music, it is better to do this through acoustics with a wooden or chipboard body. This will be a good option. Such speakers do not rattle, they have virtually no sound distortion, and they provide decent sound quality. But this should not be the main buying argument.
Now you know that when choosing a speaker system you cannot limit yourself solely to price, external design and color. We hope that this article will help you choose an option that suits your needs and discard unnecessary options.
Power
A parameter that affects the strength and volume of sound. Measured in watts. Power is divided into several subtypes:
- Nominal – at which the device operates without overload and sound distortion;
- Maximum – at which the speakers will continue to function, but signal distortion is possible;
- Peak power is the power that the device can withstand for a short period of time and not fail.
For a small room, acoustics with a rated power of 50 watts are sufficient.
For a gaming studio or a living room or home theater, 100-watt models are suitable. It is also worth mentioning “Chinese watts”. They were measured using the PMPO system and indicated a load sufficient to cause the electronics to burn out. At the same time, a multimedia speaker system for an office, the size of a pack of salt, could proudly bear the 500W label.
Currently, PMPO is hardly used - even semi-legal underground electronics manufacturers have switched to the RMS system.
And the most important thing to remember is that the power of the device is measured in watts, but not the strength of the sound it produces. Measuring its quality in this way is the same as determining the “coolness” of a camera based on the number of megapixels.
Amplitude-frequency response
In this topic one cannot fail to mention such a concept as frequency response. What it is? This is a diagram that characterizes the dependence of the amplitude of sound on its frequency. Using it, you can determine at which frequencies the speaker can play louder and at which frequencies quieter.
In other cases, I recommend choosing speakers based on their frequency response, depending on what sound you prefer:
- With a rise from 20 Hz to mid-bass for those who like to “boom” - fans of drum'n'bass, breakbeat, dubstep, death metal, grindcore and some doom metal movements;
- With a predominance of mid frequencies - for fans of classical vocals and music;
- High frequencies - for fans of heavy metal, power metal, and pig scream vocals.
To the logical question of how to change the frequency response of an acoustic system, the only adequate answer is to re-solder it yourself, replacing the base speakers with more suitable ones. However, many music lovers know how to increase high frequencies and remove bass.
The first way is to use the controls on the speaker system itself. If these are not provided by the design, I recommend listening to music using a player with a built-in equalizer - for example, WinAMP or AIMP.
It is found in the middle class and more expensive devices. However, many manufacturers provide all the necessary data for each device on the official website.
Frequencies from 15 kHz and above: why and why
Lately, when re-reading the specifications at night, I’m amazed at what ultrasonic distances modern acoustics, amplifiers and sources have rushed into. At a time when empty Marlboro cigarette packs and Technics advertising brochures were passed on by inheritance, all the luxury of audio splendor fit into the treasured 20 Hz - 20 kHz.
Today, if you flirt like a Rolls-Roys with engine power, if you don’t show a picture contrast of one in a million, you will be sold under the hammer. Against this background, conservative stereo manufacturers look modest: just think, in speakers they now indicate an upper limit of 30 kHz, but in amplifiers they have raised the bar only five times - to 100 kHz. What does all this mean, what was it done for and how should we feel about it?
The so-called “high frequencies” have a long history and have entered, one might say, into the realm of folklore. Any idiot who is infinitely far from the torment of listening to a cable is able to make a complaint - “something is not high enough.” In the days of magnetic re-recordings, the treasured “click” was sorely lacking, and what was available melted away on the harsh mechanisms of domestic cassette players, like snow in the spring. Almost all amplifiers had two adjustments. The bass was served by a knob of one hundred hertz, and to make everything “sound human,” the second band control of 10 kHz was turned up to maximum.
For sophisticated fans of distorting the amplitude-frequency response, separate equalizers were produced, in which the sliders, as a rule, were checked, lifting up the edges of the range and dropping the mid frequencies. With the “sadomaso-equalizer” turned on, magnetic dubbing was also carried out. No one cared about phase distortion. Today, according to component specifications, problems with high frequencies are long gone. I can say from myself that with digital content, at least the characteristics will not go anywhere, and the music will sound consistently good. Or consistently bad, haha. So, after all, how to treat the brisk characteristics from zero to one hundred kilohertz?
According to the rules of good form, frequency range numbers should be observed and unevenness (in decibels) should be indicated. Not everyone bothers to do this, headphone manufacturers are especially guilty. The frequency range limits given in the specifications do not say anything in themselves; they only indicate that a technical signal of the so-called “pink noise” was applied to this device. It is possible, without indicating the unevenness, to record at least from zero to 500 kHz for the radio receiver.
For adequate, uncolored sound, it is important that the response be as linear as possible, i.e. had the same level on each strip. For amplifiers and sources, the maximum unevenness is plus or minus 0.5 dB, for acoustics - 3 dB.
Since the 90s, tone controls have been removed from harm's way in high-end. And they did the right thing, by the way, although they would not have hurt in the AC. When installed in a real room, the speakers exhibit much larger peaks/dips in the frequency response than 3 dB, and advice to level out ugly sound with a network cable looks like a complete mockery.
It is officially believed that a person is able to distinguish sounds from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. This is the same as the CD playback threshold - half the sampling rate of a 44.1 stereo signal, i.e. 22.05 kHz. In 24/192 high-res, the upper limit value can theoretically reach 96 kHz, which in practice no one does: no one wants to sample emptiness, inflating an already large file. Currently, both commercial and home-made recordings (for example, vinyl rips) in 24 bit/96 kHz are most widely used. Up to 48 kHz frequency range can accommodate anything and anyone. But who will go there?
If you order a hearing test from a local audiologist, you will usually receive an audiogram up to 8 kHz, and the device will not draw anything above that, it is not designed for this. Doctors believe that for a normal life more than 8 kHz is not necessary. The famous so-called “ultrasonic” dog gag on the final groove of the 1967 record was recorded at a frequency of only 15 kHz. You can get test signals and try to hear the HF, starting with ten. For some it will be an unpleasant surprise to stop at 16 kHz, but do not rush to get upset.
The famous so-called “ultrasonic” dog gag on the final groove of the 1967 record was recorded at a frequency of only 15 kHz
With the exception of the wind organ (10 kHz), which can also produce the lowest sounds, not a single instrument plays above 4 kHz, not even the piccolo flute. Another thing is overtones: they can climb higher - up to 16 kHz for vocals, violin and piccolo. The region from 14 to 20 kHz is responsible for creating “air” in the phonogram. And the people’s favorite “clack” of cymbals quietly fits much lower – in the range from 7 to 12 kHz. It was all these small numbers that the manufacturers of stereo equipment in the 70s were guided by.
What then is in HD recordings above 20 kHz? You never know. They say that in the ultrasonic region there may be some previously unaccounted for, and therefore wildly valuable, overtones that a person (especially one as suspicious as an audiophile) is able to feel, if not hear . If you look at the frequency of an HD track, the picture is different. Some people see the use of a filter at the same sacramental 20 kHz, but then there is nothing. Some people experience life up to 48 kHz. What could it be?
As a rule - ultrasonic quantization noise, some kind of resonance, for example, vinyl cartridge systems. Does this mean that audio 24/96 and higher is a deception of the people? It doesn’t mean at all, because we get not only an expansion of the frequency band, but also the removal of quantization errors to a farther place where they cannot be heard, and an increase in the dynamic range reserve. Simply put, an HD soundtrack is more difficult to spoil when recording, so even vinyl rips at home on 24/96 sound more intelligible and expressive than on standard 16/44.1. So even though we can hear, God willing, up to 18 kHz, it’s better to listen to music in HD editions. Whatever you say about CDs.
Comparison table of characteristics
For a more clear comparison of the models presented above, we use a comparative table of characteristics.
| Model | Power, W) | Frequencies (Hz) | Noise reduction (dB) | Weight, kg) | Price, rub) |
| OKLICK OK-127 | 6 | 160-20000 | 30 | 1.6 | from 959 to 1,509 |
| Edifier R980T | 24 | 70-20000 | 85 | 2.3 | from 1,211 to 1,872 |
| SVEN MS-302 | 40 | 40-20000 | 75 | 3.7 | from 3,216 to 4,019 |
| Edifier R1280T | 42 | 75-18000 | 85 | 2.8 | from 5,785 to 6,454 |
| Dialog AP-225 | 65 | 20-20000 | 80 | 4.8 | from 4,312 to 5,220 |
| OKLICK OK-441 | 50 | 35-20000 | 85 | 4.4 | from 4,993 to 5,695 |
| Creative Pebble | 8 | 50-20000 | 75 | 3.1 | from 1,568 to 2,209 |
| OKLICK OK-162 | 8 | 150-20000 | 45 | 1.3 | from 1,120 to 1,892 |
| Edifier R1580MB | 42 | 55-20000 | 85 | 2.6 | from 4,128 to 5,569 |
| OKLICK OK-128 | 6 | 150-20000 | 60 | 0.6 | from 487 to 702 |
See also Edit
- Frequencies
- Batch frequency
- Radio emissions
Citation error No matching tag found for existing tag Community content is made available under the terms of the CC-BY-SA license unless otherwise noted. Radar antenna Opacity of the Earth's atmosphere for various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including radio waves. Animated diagram of the emission of radio waves. About the film, see Radio Wave (film). Not to be confused with radioactive radiation.
Radio waves
— electromagnetic waves with frequencies up to 3 THz, propagating in space without an artificial waveguide. Radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum range from extremely low frequencies all the way up to the infrared range. Taking into account the classification of radio waves by range by the International Telecommunication Union, radio waves include electromagnetic waves with frequencies from 0.03 Hz to 3 THz, which corresponds to a wavelength from 10 million kilometers to 0.1 millimeters.
In a broad sense, radio waves are all kinds of wave processes of the electromagnetic field in equipment (for example, in waveguide devices, in microwave integrated circuits, etc.), in transmission lines and, finally, in natural conditions, in the environment separating the transmitting and receiving antennas.
Radio waves, being electromagnetic waves, propagate in free space at the speed of light. Natural sources of radio waves include lightning flashes and astronomical objects. Artificially created radio waves are used for fixed and mobile radio communications, radio broadcasting, radiolocation, radio navigation, satellite communications, organizing wireless computer networks and in countless other applications.
Depending on the frequency (wavelength), radio waves are classified into one or another radio frequency range (wavelength range). You can also classify radio waves according to the method of propagation in free space and around the globe.
Purpose
The first and most important thing is to determine why you plan to purchase it:
- personal computer;
- home theater systems;
- music player.
Estimate the volume of the room where it will be installed. The required power, dimensions, and, accordingly, the budget will depend on these two factors.
System selection
According to the range of reproduced frequencies, acoustic systems are divided into the number of bands. If you are not a music lover and you don’t have any special requirements for quality, then a single-way system is suitable for you - one speaker works for all sounds. This is the simplest, budget option. But the most common are two and three-way. In the first case, one speaker will have one mid and low frequencies, the other will have high frequencies. In three-band, each range has its own speaker. The more bands a system has, the better the sound.
Power
Let’s be clear right away – volume and power are two completely different parameters. In essence, power determines the mechanical reliability of the system. The higher this indicator, the speakers will last longer.
Sensitivity, frequency range
Sensitivity is the parameter that really determines volume. It is measured in dB and shows how strongly the sound affects the surrounding area. Higher sensitivity means louder, more powerful sound. It is measured at a distance of a meter from the speaker using a 1 kHz sound supply with a power of 1 W.
The human ear detects a sound signal in the range of 20Hz – 20kHz. In this case, low frequencies are in the range of 20-150Hz, medium - 100-7kHz, high - 5kHz-20kHz. If you are looking for acoustics for a home theater, then frequencies within 100-20 kHz are sufficient
For universal use, it is worth considering acoustics with an extended range - 20-35 kHz
How the level of the output signal depends on changes in frequency is shown by the amplitude-frequency response (AFC). The ideal shape of the graph is straight, passing at the rated power level. But in practice this does not happen. The closer the frequency response graph is to a straight line, the better. Any sudden changes indicate that the acoustics are distorting the sound
Harmonic distortion factor
This is a very important characteristic, which, however, also rarely appears in the speaker parameters. Methods for measuring it are not entirely correct. And yet, for high-quality models it does not exceed one percent; for good-quality speakers it is a third of a percent (0.32% - 0.37%) in almost the entire frequency range, and only at the bottom this parameter can exceed 1 percent. If we consider that it is at low frequencies that our ears are not very susceptible to distortion, then such a “jump” is not critical.
Another feature: the THD increases sharply at high volumes. It should be understood that in the audio path "source - intercom cable - preamplifier - intercom cable - final amplifier - speaker cable - speaker", it is the speaker system that is the source of the most serious distortions, although it would probably be worth talking about distortions in more detail in connection with amplifiers.
Gearbox - 4B5B data coordination
Protocols using the NRZ code are most often supplemented with 4B5B data encoding. Unlike signal encoding, which uses a clock frequency and moves from pulses to bits and vice versa, data encoding converts one sequence of bits into another.
The 4B5B code uses a five-bit base to transmit four-bit information signals. The five-bit scheme produces 32 (two to the fifth) two-digit alphanumeric characters having a decimal value from 00 to 31. Four bits or 16 (two to the fourth) characters are allocated for data.
The four-bit information signal is recoded into a five-bit signal in the transmitter encoder. The converted signal has 16 values for transmitting information and 16 redundant values. In the receiver decoder, five bits are decoded as information and service signals. Nine characters are allocated for service signals, seven characters are excluded.
Combinations with more than three zeros are excluded (01 &— 00001, 02 &— 00010, 03 &— 00011, 08 &— 01000, 16 &— 10000). Such signals are interpreted by the V symbol and the receiver command VIOLATION - failure. The command indicates an error due to high interference or transmitter failure. The only combination of five zeros (00 & - 00000) refers to service signals, means the Q symbol and has the status QUIET - no signal on the line.
Data encoding solves two problems: synchronization and improving noise immunity. Synchronization occurs by eliminating sequences of more than three zeros. High noise immunity is achieved by monitoring received data over a five-bit interval.
The cost of data encoding is a reduction in the transmission speed of useful information. As a result of adding one redundant bit to four information bits, the efficiency of frequency use in protocols with MLT-3 code and 4B5B data encoding is reduced by 25%, respectively.
When using MLT-3 signal coding and 4B5B data together, the fourth transmission actually works like the third - 3 bits of information per 1 hertz of signal carrier frequency. This scheme is used in the TP-PMD protocol.
Maximum sound pressure
In the technical parameters of user acoustics (as opposed to professional models), this indicator is rarely indicated. Maximum sound pressure is naturally also measured in decibels and can obviously be indirectly calculated from sensitivity and maximum power data.
Without deliberately delving into the details and conditions for measuring these parameters, we will only say that in order to obtain the full set of impressions from audio, a limit of 90 dB is considered more or less established - at this volume (fixed, as a rule, a meter from the emitter, at that time , as listeners are located much further away), many test reports recommend performing a listening test. For comparison, sets of disco equipment for halls operate at levels up to 130 (tops) – 140 (subs) dB. This is a level approaching the pain threshold. Serious home speakers, on average, produce a maximum of 100-110dB, and for goodness sake, have pity on your neighbors!
Nothing personal, just marketing
Instead of an introduction
The truth is that the characteristics written on the box are largely a marketing ploy. This is possible due to the fact that there are no strict standards for measuring headphone parameters. Each manufacturer has its own measuring stands (precisely stands, some headphones of the same brand can be measured on one stand, others on another), and the characteristics can be given in different units of measurement.
Separately, I would like to note the characteristics of Chinese TWS headphones - cheap clones of AirPods (type i12)
When choosing such headphones, you should not pay attention to the characteristics at all. After all, they are obviously fakes or almost fakes, sold only because of their appearance
The quality of the components (including the speakers) and the build in this case is so poor that it makes no sense to look at any specifications.
Of course, the universal principle “the more numbers, the better” still works, but with some reservations. Let's take a closer look at the main characteristics of the headphones. Let's not get into the nuances, there are very, very many of them. Let's try to arm ourselves with basic concepts that will really help in choosing headphones.
- TOP 15: Best headphones for music
Types of columns - brief description
Any speaker system consists of a configuration that can be designated by the numbers 2.0, 2.1, 3.1,5.1, 7.1. The first number in this marking indicates the number of speakers (satellites), and the second indicates the presence of a subwoofer. That is, if the speakers are designated as 2.0, this means that they do not have a separate low-frequency speaker (subwoofer), and the lower bass is built into the speakers themselves.
Dividing the system into main speakers and a subwoofer allows you to get higher quality, surround sound, creating the effect of presence. The more accompanying speakers the system has, the better and more impressive the sound.
Let's look at what types of columns exist:
- Computer. The simplest and most budget-friendly PC speakers do not have a subwoofer. There are those that consist of a 2.1, 3.1 system. As a rule, computer speakers are small in size and designed for desktop placement. The speakers can be connected not only to a desktop PC, but also to a laptop, tablet, or smartphone.
- Floor-standing. These are more powerful and larger audio systems used in home theaters and large rooms. To reduce vibrations on the floor and walls and make the sound clearer, floor-standing speakers are equipped with special stands made of stone (granite, marble). Cheaper models have rubberized stands. The floor-standing type of acoustics is more sensitive than others and is more demanding on amplifiers.
- Ceiling. Not too large speakers placed under the ceiling can be used both as front satellites and as two-channel audio systems. They are suitable for small spaces and are very practical because they take up little space.
- On racks. These speakers are placed on the floor, but differ from ordinary floor-standing ones. They are not large, and their speakers are designed to be installed at a certain height. It is thanks to the correct placement that you can get spectacular, surround sound. The height of the stands in most models is adjustable.
- Soundbars. The difference between such acoustics is that all elements and channels are located in one horizontal panel. Externally, the speaker looks primitive and simple, but in terms of sound quality it can surpass 5.1 and 7.1 systems. This effect is achieved thanks to high-tech algorithms that supply signals from the amplifier to the speakers separately. This is one of the most expensive types of home audio systems.
- Portable. Usually this is just one column that can work autonomously from 4-5 to 20 hours. Connection with devices occurs via Bluetooth. This type of acoustics is intended for use in a small room or outside the home. Portable speakers have become an excellent solution for recreation; they are loved by young people and travelers. High-quality mobile speakers have quite powerful, clear and spacious sound. Although, of course, this cannot be called a full-fledged audio system.
These are the main types of home speakers that can be purchased today on our market.
Wireless speakers
Wireless (portable) speakers connect to a smartphone, tablet or other device via Bluetooth (the most common version is 4.2). This gadget takes up minimal space and provides high-quality sound. As a result, you can listen to your favorite music while traveling and hiking, on the beach and at parties with friends.
Portable speakers also provide a wired connection to mobile devices (via mini-Jack). This connector also allows you to connect headphones to the device. A wired connection uses less battery power.
Main parameters:
- number of channels – the more, the more voluminous the sound (1.0 – mono, 2.0 – stereo, 2.1 – stereo with subwoofer);
- number of bands - must correspond to the number of speakers; if there are more bands, the sound quality will be very low;
- power – depending on the model, ranges from 1.5-120 W;
- frequency range - the wider, the higher the quality of the reproduced sound (lower frequencies - 20-500 Hz, upper frequencies - 10000-25000 Hz);
- volume – the minimum setting is 80 dB, but it is better to take a model that produces 95-100 dB (enough for a spacious room).
Nutrition
The vast majority of portable acoustics have a battery, but there are models that run on batteries. Such gadgets are lighter and do not require an outlet. The disadvantage is the cost of purchasing batteries. Wireless speakers can be powered from the mains (220V) and PC/laptop (via USB port).
Battery capacity – determines the continuous operation time of the device. The unit of measurement is milliampere hour (mAh). The larger the battery capacity, the longer the music will play. The standard version is 2200 mAh and lasts for 10 hours. This parameter is especially important if the speaker will be used outdoors.
Housing material
Most often, the body of wireless speakers is made of practical and relatively cheap plastic; metal and wooden options are much less common. Dust- and water-resistant models use rubber and silicone, which also withstand impacts well.
Additionally
The dimensions and weight of portable acoustics also matter. For sports and outdoor activities, it is better to choose a compact and lightweight model with a carabiner or other reliable mount. If the speaker will be at home or in the office, then give preference to a weighty gadget that provides better sound.
Wireless speakers are most often used outdoors
Therefore, when choosing, you should pay attention to protection from dust and moisture. This characteristic is indicated as an IPXX code, where the first digit indicates the degree of protection against dust, the second - the degree of moisture protection
Dust (sand) protection:
- IP4X – protection against objects measuring 1 mm or more;
- IP5X – dust-proof housing;
- IP6X – dustproof housing.
Moisture protection:
- IPX1-3 – protection against vertical drops, practically useless;
- IPX4 – protection against splashes from any direction (rain);
- IPX5-6 – protection against jets/strong jets (heavy rain, downpour);
- IPX7 – the speaker can withstand short-term immersion to a depth of up to 1 m (accidental fall into the pool);
- IPX8 – the speaker can withstand prolonged immersion to a depth of more than 1 m (residence time is more than 30 minutes).
Portable outdoor speakers must have IP45 or IP56 protection. But for the beach or fishing it is better to take a more reliable model with IP67 or IP68.
Important: manufacturers guarantee protection against exposure to fresh water. But sea water or water with various chemicals can damage the column
Full waterproofing increases the cost of the device and degrades the sound quality - it becomes quieter and dull.
Vibrating speakers are a type of portable speakers. This acoustic system is installed on a flat surface, which acts as a speaker (glass, furniture). Fixation on different supports allows you to adjust the “color” of the sound. Disadvantage: it only works in tandem with an item. Some regular portable speakers have a separate vibration option.
Sensitivity
In connection with all of the above, let’s move on to the “sensitivity” parameter. It is measured in decibels. This indicator, to some extent, indicates the degree of perfection of our column. In practice, this is its efficiency, its efficiency factor. For modern acoustics, this parameter is in the range of about 83-95 decibels. It is clear that high sensitivity values, especially for a classical multiband system, are achieved through many serious and often expensive technological improvements.
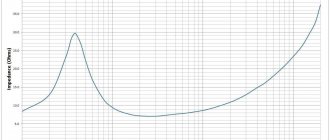
Speaker sensitivity measurement circuit
Increasing sensitivity by 6 decibels leads to the feeling that, with the same input signal, the acoustics sound approximately twice as loud! And by the way, in order to raise the volume by 3 decibels, the speaker cone must vibrate with approximately twice the amplitude. For a low-power amplifier, and this, in particular, is the majority of tube models, the sound of which is so attractive, you need acoustics with high sensitivity.
Best lists
Today you can find a large number of different speakers on sale, so we decided not to stop focusing on the rating and additionally organize a list of the best in three categories:
Let's take a closer look at these nominations and the models described in them.
Budget price
Defender SPK-22 is a miniature device designed for a laptop. Their power is 5 W. The minimum/maximum reproduced frequency is 200 and 18000 Hz, respectively. The speakers do not require a power supply; they operate from the USB connector of the computer. Output – linear (stereo). To supply sound, they must be connected to the audio jack of a personal computer. The device is made in black color scheme. Distinctive features: compactness, lightness, attractive design, durability.
Price from 175 rubles.
With subwoofer
Powerful Logitech Z-623 speakers, the total power of which reaches 200 W, have clear, rich sound and a fairly large volume reserve. Scheme of the acoustic design of a passive subwoofer - bass reflex. Volume and bass toggle switches are located on the right satellite, there is also a power button, a headphone jack and a mini-jack input
The manufacturer paid great attention to the design - the exquisite shape of the satellites, combined with the simplicity of the subwoofer, will become an effective interior decoration
Cost: from 13,000 to 15,000 rubles.
Wireless
SVEN SPS-750 is a powerful and presentable home stereo system, consisting of two two-way speakers in black MDF cases. This acoustic system is equipped with a built-in Bluetooth adapter, providing convenient wireless synchronization with mobile devices, PCs, and laptops. Using a detachable cable with 3.5 Jack and S/PDIF connectors, the speakers can be connected to playback equipment wired. The power of each speaker included in the SVEN SPS-750 stereo system is at the level of 25 W, and the total output power of the speakers reaches 50 W.
Cost: from 5,000 to 6,000 rubles.
A little theory
Sound is the propagation of mechanical vibrations in a gaseous or liquid medium. Like any wave, sound has parameters such as amplitude (characterizes volume) and frequency (characterizes tonality).
The average person's ear can detect sound with frequencies ranging from 16–20 Hz to 15–20 kHz. In turn, this range has three “steps”:
- 20–150 Hz – low frequencies.
- 150‑7000 Hz – mid frequencies.
- 7–20 kHz – high frequencies.
The higher the vibration frequency, the higher the pitch of the sound. For example, a bumblebee, which flaps its wings slowly, hums, and a mosquito, the frequency of whose wings flapping is significantly higher, squeaks vilely, hiding in the darkness.
Sound below the audibility range is called infrasound, from 1 GHz ultrasound. The human ear does not perceive them, but such sounds with a large amplitude can have an effect on the body.
In addition, with age, almost every person is susceptible to senile hearing loss, when high-frequency sound is not perceived. Biologically, it is determined that women perceive high frequencies better, and also better distinguish intonations and tones, which is influenced by the need to care for offspring.
For the same reason, most of the fair sex are difficult to deceive - they are able to detect any falsehood in the voice. It is also worth noting that in women, hearing begins to deteriorate by the age of 40, while in men this process starts at 30.
In relation to speakers, the sounds of human speech and music are primarily of interest. There are significantly fewer aesthetes who listen to the sounds of wildlife on the computer compared to film buffs and music lovers.