What is the difference between two-way and three-way speakers? What do these stripes even mean, and what do they affect? The article will answer these questions. She says:
- about what broadband speakers are;
- about types of speakers;
- about the crossover and its significance.
All this will help you choose the best speaker system, based on the requirements for sound quality and the actual purpose of the speakers.
Comparison of two- and three-way speaker systems
Modern people love to listen to music in their free time, at home, on vacation, on the road, and wherever there is such an opportunity. Many sound-reproducing devices have been created for these purposes. Today, speakers, which are essentially a kind of acoustic systems of different bands, are popular among buyers. The most popular niche in the market is occupied by two-way and three-way speaker systems (AS). It is about them, their differences, advantages and disadvantages, as well as technical characteristics that will be discussed in our material.
How to choose acoustics.
I haven’t posted anything for a long time, it even feels awkward in front of my subscribers. So I decided to dilute my little blog about making acoustics with a related topic - choosing an acoustic system for music. When choosing speakers, a person far from audio engineering is faced with the difficult task of how to choose the ideal acoustics for his budget. There are a ton of models on the market, of all shapes and colors, and almost every one receives praise in audio magazines and on thematic websites. And it’s not clear what to choose, this speaker has 3 speakers, and it costs 20,000, and the other has 3, and costs 200,000. It’s precisely the features of speaker systems that I want to help an unprepared music lover understand.
A small disclaimer. All indicated advantages or disadvantages of the speakers described below are purely analytical in nature and do not constitute a 100% statement regarding a specific acoustic model. I will try to describe the basic principles of choice, something like, you don’t need to take a car with square wheels. All advice serves only to push an inexperienced person along the right path in making a choice. The final decision to purchase a particular model must be made after listening.
So where to start. Let me start with some philosophy of choice. First of all, when choosing, the first thing to remember is to think with your head and listen with your ears. Under no circumstances should you trust articles and tests from magazines; I have never seen bad articles or tests, but there is a sea of bad acoustics. Second, do not trust reviews on the Internet. If a person has not heard anything better in his life except all sorts of Sven microlabs, then any acoustics of a higher category will seem superb to him. There are probably 70 percent of flattering reviews about poor acoustics on the Internet. Better read negative reviews; repeated shortcomings among different people are already a certain argument.
Speaker Bandwidth
Acoustic devices presented on the domestic market differ in their scope of application: for musical instruments, studio devices, for television, home theaters, and automobiles. All listed speakers differ in technical characteristics and other consumer qualities.
Thus, the most important technical parameters of any type of acoustics include banding. Not all buyers understand what this term is, so it is logical to give a brief explanation. Bandwidth indicates the width of the range and the number of speakers used to separate frequencies in acoustics . According to this definition, the main classification of devices is built into:
What is the number of bars on the columns?
Band
means a separate range of the entire frequency spectrum that is reproduced by car speakers.
Each strip
corresponds to a speaker/s. Multi-way speakers sound better than broadband (single-way) speakers.
Interesting materials:
How to remove encrypted LG channels? How to remove Freezing a table in Excel? How to remove pinning in Viber? How to remove frozen rows in Excel? How to clean the waiting room in Zoom? How to remove stuckness on a laptop? How to remove text fill from the Internet in Word? How to remove text fill when copying? How to remove text fill in PowerPoint? How to remove text fill in Word?
Differences between 2-way and 3-way speaker systems
Wideband acoustics operate according to the following sound reproduction scheme:
The main difference between two-way acoustics is the absence of a subwoofer. The midwoofer is responsible for the reproduction of bass, as well as mid-frequency sounds. Whereas the counterpart with 3 bands is characterized by a clear frequency separation between the speakers .
By purpose
Single-way speakers are most often made in a portable version and are used to amplify sound on vacation, in nature. Two-way models are also available in a portable version and are used for sound reproduction in most cars. Stationary wired systems of this type for computers are also produced. While three-way speakers are most often stationary devices for listening to music or watching movies on TV or a home theater.
According to technical characteristics
Depending on the technical solutions, audio equipment is divided into active and passive. In active sound sources, each speaker is equipped with a signal amplifier.
The sound of the speakers depends on the type of speakers used in the specific model of speakers. Thus, sound sources are divided into coaxial and component. The first type of sound system is a single design that includes cross-frequency separation and LF, MF and HF drivers. In this case, sound reproduction is narrowly targeted. Whereas component multi-frequency speakers of a sound system can be located in different places in a room or car, resulting in surround sound.
By price
The issue of cost is also significant when choosing acoustics. It is cheaper to purchase and install 2-way audio equipment. The savings are due to the smaller number of components: two speakers, one cross-filter and a pair of amplifiers (depending on the model). In addition, you can install the system yourself, without involving specialists - just basic knowledge and skills in electrical installation are enough.
To buy a three-way sound system, the buyer will have to spend money not only on a more complex set of equipment, but also on its installation. It is impossible to do without the help of a professional, since installing and configuring such a speaker requires special measuring instruments, as well as an ear for music. Otherwise, you won’t get surround realistic sound after installation.
By other parameters
It should be noted that three or more band sound systems belong to the Hi - Fi . The decoding of the abbreviation High Fidelity in translation means a high level of sound quality, but in practice the resulting audio signal is almost identical to the original.
Why do we need full range speakers?
There is no need to explain to anyone why wideband speakers are needed - these are the main speakers of any audio system, not just a car. Why you need a wideband speaker in a car that does not have an audio system is clear to everyone. But why might a car enthusiast whose car already has a standard audio system need it? Because manufacturers often save money on an audio system by installing inexpensive single-way speakers, which still somehow pull out the midrange frequencies, while mercilessly cutting out the “tops” and, especially, the “lows.” You don’t have to be a music lover to notice the disappearance of the bass guitar in your favorite composition, and an inexpensive “one-way” speaker can easily provide such a trick. The easiest way to save the situation is to replace the standard speakers with coaxial ones or higher-quality broadband ones with an extended frequency range.
But still, the most common reason for replacing a standard (sometimes even coaxial) speaker with a wideband one is the creation of component auto acoustics, i.e., an audio system in which the sound is divided by frequency and each frequency band is voiced by a separate speaker: HF - tweeters, MF - wideband speakers, LF - subwoofers. So far, it is component car audio that is considered the best solution for ensuring purity and sound quality.
Advantages and disadvantages of popular speakers
The popular systems with frequency division into 2 and 3 speakers have their advantages and disadvantages, relating not only to sound reproduction. Also taken into account: form factor, complexity of installation and configuration, materials, price and other technical and user criteria.
Pros and cons of a two-speaker system
Two-way speakers are most in demand at the household level due to their many positive qualities. But there is no limit to perfection.
| Positive sides | Negative aspects |
| Compact sizes. | The sound quality is significantly inferior to three-way systems. |
| Affordable price. | |
| Easy to install and configure. | |
| Possibility of self-assembly. | |
| Sound reproduction is of good quality. | |
| Availability of a wide range of models for various purposes of use. |
Pros and cons of 3-way speakers
Three-way speakers are semi-professional level and above, where the highest sound quality is required. These systems are in demand among audiophiles for their advantages. However, the complexity of the equipment also entails disadvantages.
| Positive sides | Negative aspects |
| Volumetric, close to realistic sound. | Difficult to install with a large number of components. |
| Possibility of use in clubs and concert venues. | |
| Flexible adjustment of uniform distribution in the room. | The dimensions are far from compact; sufficient space for placement is required. |
| Functionality. | Higher cost of equipment. |
Conclusion
Thus, we can draw a completely logical conclusion that will help the motorist choose acoustics with the required number of stripes for his favorite car without overpaying and additional problems.
The selection formula is quite simple:
1. If you need very high-quality car audio, it is better to buy and install expensive three-way speakers and a separate subwoofer; 2. If you need to do it inexpensively, but with high quality, you should install two-way speakers with a passive subwoofer; 3. If you have a minimum of money, it’s better to get by with single-way pre-installed “tweeters” for high frequencies, supplementing them with inexpensive 2-way speakers with low-frequency coverage.
Experts from the CarWorks workshops located in the capital will help you make the right and technically competent choice, where you can inexpensively install car audio in a car with the selection of the most suitable and high-quality components from brands that have proven themselves on the Russian market.
Also, if you contact us by appointment at the most convenient time, you will be able to:
Share on social media networks
Car owners quite often, when choosing car audio for a car, are faced with the question of which one.
Where is it better, easier and cheaper to buy car audio for a car with complete installation?
Source
Which choice is better
To decide which acoustics are best for home, family or outdoor events, and which speakers are best to buy for professional use, it is recommended to carefully compare the technical characteristics of the devices (in particular, power, sensitivity, etc.) and pay attention to the materials. Of course, the higher the bandwidth, the brighter the audio picture will be reproduced. But this also comes with some operational difficulties. However, if you absolutely want to enjoy surround, bright sound, and your budget allows, then within 15-20 thousand rubles you can purchase a three-way speaker system of decent quality.
Source
p1meter = SPL + 10*lg(P), dB
p 1meter - Sound pressure level (1meter)
SPL - Speaker sensitivity
P - AC power
This formula shows that each doubling of power increases the sound pressure level by 3 dB. The resulting value of the sound pressure level will be valid when the listener is at a distance of 1 m from the speaker. The sound pressure level at the design point is determined by the expression:
Three ruble or two? - that is the question! For those who make this choice...
I assume that the text below will be relevant for the FAQ because... This question is asked by many beginners and not only fans of Auto Sound, and almost everyone makes mistakes in three-way systems and very often.
*the question is, of course, relevant, but this will not be included in the fact sheet, due to numerous inaccuracies, including in the “axioms”. Please do not consider this an official FAC! MiX
Below I will give speculations in favor of one system or another. Perhaps they will remove many questions regarding the construction of their own music system in the car.
Which is better, a two-way system or a three-way system? When should you start building a three-lane system, and when should you avoid it?
To begin with, I will give a few AutoSound axioms. Without awareness of them, you may not even be involved in AutoSound at all. these are the ABCs and postulates.
AXIOM No. 1
- any automotive system must be connected channel by channel, the source or external processor must provide the necessary delays for each channel, set the slope and cutoff frequency (we carefully read not only the frequency, but also the slope of the cutoff!), and of course the processor or source must have an advanced good equalizer.
- for example, if you want to build a so-called 2+ system (this is when the mid and high frequencies are connected via a cross), then this is a stupid task because You won't be able to mix the mids and highs correctly. in this case, it’s better to just make a two-way system because it will do any 2+ (statistically on average).
- for example, if you don’t have money for an external processor (of the currently commercially available and popular three-ruble rubles, these are the bit one, the alpine 800th (external processors) and the 99th pioneer, like a separate radio). The cost of any of them is not less than +-29 thousand rubles (new). If it’s a pity for you to pay such prices in order to start driving three rubles, then you forget about it at the moment. otherwise nothing meaningful will happen.
Axiom No. 2
— the three-way system is relevant only when the midrange link is installed on top of the torpedo or on its border at the top. That is, if the midrange is installed in the doors (for example, a standard place in many BMWs or Mercs) - this scheme is more detrimental. The place under the midrange is so bad that such an installation will do more harm than good. The midrange should always be mounted at the top and directed toward the listener, not to the side.
— if you want to push a mid-range driver into a regular place in the doors (for example, a BMW or a number of other cars), then it’s better for you to refuse three rubles because in such a performance there will be more harm than benefit from the midrange. The installation of the midrange is relevant only in the area of the upper part of the dashboard (when directed towards the listener) or above the dashboard on the racks or in the dashboard itself from above with the direction towards the glass.
- if the standard place under the midrange is in the dashboard itself from above and is aimed at the windshield, then you need to take into account another point: if the windshield of the car is tilted very strongly, then you can catch a large amount of re-reflection (stand-up) and the harm from this may be more than good from midrange Accordingly, when installing the midrange speaker in the dashboard (when directed upwards), you should always take into account the fact that it is advisable to turn the midrange a little more towards the listener in order to avoid stand-ups and other hemorrhoids (there can be enough hemorrhoids even without stand-ups).
Axiom No. 3
— The midrange speaker must certainly be a diffuser and preferably with a large diffuser diameter (10cm in some cases, if you really want it, then 7cm is possible). Why not a dome? The dome will not allow you to reveal the true potential of the three-way system because will not allow the mid to load a purely low-frequency link; moreover, the cutoff frequency with a dome midrange will always be at an “inconvenient” frequency in the region of 600-1200 hertz, where the most important “hertz” are located, which are not optimal to “rip” with different speakers. In any case, a competent system with a dome midrange will be better than a similar two-way system, but again, I wouldn’t call it a full-fledged three-way system because I put a different meaning into the three-stripe (complete “Squeeze” of everything possible).
— conclusion: in a three-way system it is best to use 10 cm diffuser-type midribs. A 7 cm midrange may not play as low as a 10 cm one, but nevertheless it will still be relevant, albeit smaller. Dome midranges are already a kind of extreme, where, by and large, a big question is raised about how relevant a dome midrange is in the system. In my opinion, it’s easier to build a two-polka with the same money and she will make one three-ruble. Why then do we need dome midranges? In my opinion they are not needed. Although some of these midranges can be used as shiriki (wide-field speakers as part of, again, a two-pole system). A dome can also be relevant in cases where you really want a three-band system (even if you shoot it in the head), but there is no room for larger midranges.
Axiom No. 4
— a three-ruble note assembled and tuned with straight hands is ALWAYS better than a two-ruble note. Of course, it’s much easier to set up a two-way band, but with the correct settings of both, the three-way band will always be a priority by a wide margin. Even a more budget three-way system will play more seriously and better than a much more expensive two-way system.
conclusion: a three-way system is relevant only if you have already fully mastered the two-way system. We figured out how delays work, what phases are, etc. and so on. If you have little experience, then a three-way system will only discourage you from further desire to engage in Auto Sound because... It will be much more difficult to build it correctly with two lanes. Three rubles are NOT FOR BEGINNERS! You should never start with it! If you don’t have several SQ cups in your garage at competitions, then you won’t come close to coping with three-point marks (I said this in a very exaggerated way, of course). Of course, you can turn to “senior” comrades for setup if you have them in your city. Three rubles are better, but only in SKILLED, experienced hands. In other cases, the three-ruble note is terrible (well, that’s a bit exaggerated).
Aximoma No. 5
— what is a three-ruble note needed for? a) - relieve the load on each speaker in the system; the narrower the range of reproduced frequencies a particular speaker plays, the better it does it. b) - raise the playing stage and build it even more precisely, due to the location of the midrange element in a more optimal “vertical” space.
conclusion: when choosing a three-way system, choose the low-frequency and high-frequency sections more carefully. Everyone thinks only about the midrange (since the main load falls on it) and this is absolutely not true or only half true. The point of three rubles is to squeeze the maximum out of everything: bottom, middle, top. Therefore, when choosing a low-frequency link for a three-way system, you should look for very BASS speakers, and tweeters, on the contrary, that play well upward, otherwise you will burn one of the advantages of a three-way system with your own hands.
Axiom No. 6.
Midranges measuring 10 cm require an average volume of 0.8-1.5 liters. MF 7 cm +- 500 grams. These speakers cannot play ANYWHERE or do it noticeably WORSE. Moreover, these speakers cannot play at the same volume as the bass, for example.
Conclusion: — Is there room in the dashboard under the speaker for a volume for this speaker? on average, a 10 cm media requires a volume of 0.8-1.5 liters. Often in some cars it is possible to screw a midrange speaker into a regular place, but it is impossible to create the necessary volume for it there! Such a frequency will cause more harm than good.
— If you want to install the midrange on a stand, then immediately pay attention to the dimensions of the stand itself. A minimum volume of 800 grams per midrange 10cm midrange on a narrow stand can look so WORSE that even the resulting high-quality sound does not compensate for the poor appearance of the entire structure. When installing the midrange on a stand, please note that the stand should be wide and the final appearance will not be detrimental (of course, you can try to find a compromise and look for a 7 cm diffuser middle, this will require +-500 grams of volume and such a “boob” may look more optimal, although the more pleasant size of the midrange is 10 cm.) But on the stand of, for example, a VAZ 2109, even 400 grams of volume will look POOR and a good sound will no longer be worth it (except for very extreme people).
SUMMARY You should forget about the three-stripe like a bad dream if:
You do not have a sufficient budget to handle the processors that allow you to drive three-pole systems, as well as the additional costs caused by the midrange link. A three-way system is initially already EXPENSIVE and COMPLEX.
You do not have sufficient skills in setting up two-way systems and are generally just starting to get involved in Auto Sound, and in the event of an “emergency” you will not be able to find the right specialist in your city who will tell you what’s what. Moreover, the skill and understanding of AutoSound must be high and at a level not lower than “competitive”.
You don’t have a place in the car where you can install a midrange speaker correctly and without turning the car into something wretchedly terribly collective farm. Alas, a three-way system cannot be installed in some cars without “killing” the interior design.
PS I immediately warn you that it is useless to ARGUE with my axioms, that’s why they are axioms. Nevertheless, I mean that people will begin to “protest” them, then in order to avoid FLOOD I will erase such messages! BUT... if the same AXIOM is refuted a lot, later I will take it and analyze it in a separate POST, where everyone can have a lot of fun about this axiom. It will be convenient and correct, and most importantly, it will not offend anyone. EVERYONE will speak out. So there’s no point in being offended by something I’ve worn out. this shabby thing will come up in the following posts and I will not forget or ignore your opinion and questions.
all this is relevant for SQ systems, that is, for high-quality sound inside the car. If we are talking about a handle (stage, etc.) for voicing primarily the space outside the car, these rules are naturally not relevant.
PS3 for the most gifted!
All your objections and a complete debriefing on these issues will be in the next post or one of them, where I will explain your objections regarding the axioms in more detail and in more complex technical language. I wrote about this ABOVE, but alas, a number of very smart comrades (by the way, who are not at all good with physics - about this also later in more detail, indicating where exactly they are not right, just as in other things they are not always right in the head) for some reason began to write urgently and in a separate post these questions. I ask these gentlemen to calm down their schizophrenic moods inspired by the disgusting weather and wait for a separate post regarding your questions and objections. Moreover, they should not shout unfoundedly that the things written in Auto Sound textbooks and physics textbooks are nonsense. Let's just say my post is based on them. It will be more technically difficult to follow. week. Once again I ask you to wait and show mercy.
Well, for those who are especially big fans of flooding, I offer a separate video for your viewing pleasure. Let’s just say that being a fan of Philip’s work, the more pleasant it will be for me to agree with this video of his.
PS4 smart remark from C5D there are indeed many midrange speakers for which the optimal volume is more than one and a half liters. There are some - Alas, I didn’t write about this at first, but I was corrected. Accordingly, when choosing a midrange speaker, you always need to determine what displacement is optimal for it, which again complicates the process of three-thirds.
Source
Anatomy of loudspeaker systems: the wideband debate
It so happens that sometimes on our blog we raise questions that cause quite a heated, lively discussion on this and other resources. I believe that this will be the case this time too, since we will talk about an almost philosophical (for some people) question: the advantages and disadvantages of broadband speakers in comparison with multi-band ones.
I note that I am a supporter of multi-band speakers, and for a number of reasons I believe that the more bands (within reasonable limits, of course), the better. Due to the above, I may be somewhat biased in assessing the polar point of view (but I will try to maintain a neutral approach).
The essence of the controversy
The practice of using broadband dynamic emitters and speakers created on their basis has formed a stable stereotype that the wider the frequency range of an electrodynamic emitter, the lower its linearity. Accordingly, the vast majority of broadband emitters, as a rule, do not have a very smooth frequency response, and many emitters of this type are characterized by a high level of harmonics and intermodulation distortion.
This opinion is confirmed by a number of pure experiments, from the point of view of the physics of sound and psychoacoustics, conducted over the past 40 years. The experiments compared broadband and multiband speakers. Due to the presence of serious shortcomings (low linearity of components equipped with broadband emitters), the vast majority of manufacturers abandoned the wide band and began to produce multi-band acoustics.
Opponents of multi-band acoustics argue that the low linearity of the speakers of such systems is more than compensated by the absence of “terrible phase distortion” and “monstrous problems” with the linearity of crossovers dividing the sound into bands.
In other words: multiband filters “rotate the phase ungodly,” which has a “terrible” effect on the sound. In addition, it is often stated that passive crossovers can significantly worsen the dynamic characteristics of the system, reduce the detail of the sound and make it “flat”. The listed disadvantages relate mainly to passive crossovers, while the disadvantage of active ones is their cost.
Among other things, supporters of wideband speakers often appeal to certain magical-metaphysical features of the influence of the sound they reproduce. To demonstrate the “magical” effect of the sound emitted by such a speaker, I will give one quote (it fully reflects the opinion of those who appeal to “shamanism” in this matter):
“But on the other hand, without noticing it myself, after some time I switched from analyzing sound to listening to music. I played track after track, listened for an hour instead of the planned 10-15 minutes. Then a very interesting feeling appeared - I wanted to sing along with the performer, try to play a chord behind the instrument - although both were difficult to figure out after the familiar homemade work on ScanSpics =). Having turned off the equipment, I left in a very positive mood - I had the feeling that I had heard something that I had never heard before - it’s difficult to say what exactly. But it turns out that those who talk about some magical side of broadband are right. »
(spelling and punctuation preserved)
Multi-way speakers
Objectively, the vast majority of multi-band speakers have a number of advantages. Most multi-band systems with passive crossovers are characterized by:
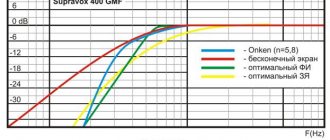
Frequency response of high-quality three-way acoustics
As I already noted, in addition to the complexity of the design and price, multi-band systems are characterized by the presence of phase-frequency distortions. It should be borne in mind that this type of distortion can only be noticeable if the group delay audibility thresholds are exceeded (which in the 2 kHz region is about 1 ms). The vast majority of speaker system manufacturers have been guided by this criterion from the mid-90s to the present time.