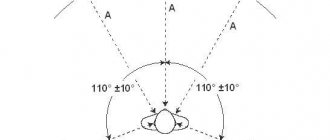
The location of the speaker system according to the 5.1 scheme
Today, 5.1 and 7.1 speaker systems have become widespread; the increase in their popularity is mainly associated with the appearance on the domestic market of home theater systems equipped with acoustic system data. Although more than 90% of these acoustics, to put it mildly, are poorly suited for high-quality sound reproduction, there are also some people who bought Hi - Fi and High - End class acoustics. Also, most music lovers do not yet have and are only thinking about purchasing such sound-reproducing equipment and speakers. Our article will be useful for these categories of people.
CD-Audio
The very first music format that changed this world forever, giving the music industry an incredible breakthrough. With him began the era of penetration of digital format into the life of an ordinary person.
CD-Audio is the same music compact disc . We owe its invention and implementation to Sony and Philips. The format itself was standardized and introduced into mass production in the 80s. The main characteristics regarding digital audio are revealed in the 16-bit signal width and sampling frequency, which is 44.1 kHz. If we talk about frequency, then its choice was not random, it was even necessary. This happened due to the fact that it was necessary to combine the invention with pre-existing audio systems, the source for which were video cassettes.
The most important quality of the new product at that time was its incredible durability . If we look at the indicators, then not a single storage medium of that time did not have such characteristics, both physical and qualitative (records, tapes). The CD can be used for years. This is explained by the lack of physical contact between the reading device and the disk. The wear and tear of previous storage media was reflected in an increase in the level of noise and defects. Here, the appearance of scratches did not affect the quality of playback. An undoubted advantage was the ergonomics of the storage medium, which simplifies its use. The new standard, almost immediately, found itself in the automotive industry, where since the 50s. tried to install music devices, but everything ended in failure. The records quickly failed, although special automobile ones were made, and large reel tapes took up a lot of space and were inconvenient to use.
The arrival of the Audio CD and its progressive sound quality marked the collapse of the vinyl record . The reason was the stated value of the dynamic range, with the signal-to-noise ratio being more than 90 dB and the distortion being 0.01%.
But still, a little later, the main drawback of the CD . The upper frequency of the Audio CD range, during playback, was equal to half its sampling frequency (22.05 kHz). This figure for competitive carriers was much higher. Even though frequencies of 19-20 kHz belong to ultrasound, that is, they are practically inaudible by humans, they could not be discounted. In most acoustic instruments, the overtonal components lie in this region and have a huge impact on the perception of what is heard. In their absence, the sound does not seem real. Based on this, it became clear that the era of sound is only at the dawn of its development, and new digital standards and formats are coming. The most interesting is yet to come.
DVD-Audio
DVD-Audio is the next stage in the development of audio media . The emergence of technology and media where more information can be recorded was reflected in the creation of a new audio format. The principle of encoding the original signal itself remained almost the same as the previous one, but this time the sampling frequency and bit depth of digital data increased. Now the digitized sound is much closer in sound to the original. Information compression is used, but without loss of quality, which leads to an increase in recording time. Thus, DVD-A can record 74 minutes of audio. With the advent of such a storage medium, it became possible to actively use sound channels, which could reach up to 6. Now electronics manufacturers have begun to adapt to this format, sensing a new niche there; a surround sound signal appears - Dolby Digital and DTS formats .
Those. DVD audio information
The audio signal is recorded using the pulse code modulation method - PCM (pulse code modulation) format. The sampling frequency ranges from 44-96 kHz, and for stereo it reaches 192 kHz. The data width ranges from 16 to 24 bits. The playback frequency range is 5 – 48,000 Hz, for a stereo signal it reaches 96,000 Hz. The dynamic range is 144 dB. The maximum amount of data is 4.7 GB on one disk layer. To compress audio without loss of quality, the Meridian Lossless Packing (MLP) . When using it, it became possible to compress the sound almost twice.
DVD-audio: main advantages of the standard
- 1. Sound quality is very high
- 2. Huge dynamic range
- 3. The number of channels reaches six
- 4. Large selection of equipment for operation
- 5. The most common encoding format in recording studios is PCM
Links[edit]
- ^ ab Jack Schofield (2 August 2007). "No taste for quality sound". The keeper
. Retrieved May 29, 2009. This format - Super Audio CD (SACD) - has existed since September 1999. And now he is dying. - "Crest National and Philips Partner to Bring US SACD Hybrid Disc Manufacturing". newscenter.philips.com. 2002-05-30. Retrieved December 31, 2011.
- Mark Fleischmann Are DVD-Audio and SACD DOA?
April 2, 2004 “The compact disc tidal wave was so aggressive that it swept away everything in its path, including the terms “album” and “record.” I keep waiting for the high definition audio to cause a tsunami like this. But the tiny islands of SACD and DVD Audio titles at my local Tower Records did not grow into mighty continents." [1] Retrieved January 16, 2010. - C | Net News, March 26, 2009. Betamax to Blu-ray: Sony's Format Winners, Losers
Steve Guttenberg. [2] “Audiophiles praise SACD, but the market has failed. Sony Records is no longer releasing new SACD titles" (This is not entirely true; Sony Classical does not appear to be releasing new SACDs, Sony Classical in Germany and SACDs were manufactured in Japan on June 5, 2009 ( Sony Classical Germany ( Sony Music Japan )) Retrieved May 29, 2009 - Stereofile e-newsletter, January 10, 2006 Io Saturnalia!
by Wes Phillips. [3] Mention is made of SACD and DVD-A's "failure to gain traction". Retrieved May 28, 2009. - ↑
Audio Video Revolution, October 19, 2006.
Jerry Del Colliano "The Symbolism of the Losing Tower
". "The sheer failure of SACD and DVD-Audio as high-definition formats was analogous to the burning of a small town." [4] Retrieved May 28, 2009. - www.hificorner.co.uk - return machine
- ^ ab "The 10 Best Audiophile SACDs, Many of Which Are Sold Out". Audiophilereview.com. Retrieved March 6, 2013.
- High precision review. News . Retrieved May 20, 2009.
- SA-CD.net
- ^ab High precision review. Universal Music artists receive SACD Gold and Silver in Europe. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
- SA-CD.net. FAQ
- Chicago Resound labels retrieved June 6, 2009
- ↑
London Symphony Orchestra - Buy Records, retrieved 6 June 2009. - Rhianna
Sinclair, Paul (30 January 2013). "Top 10: SACDs You Can Afford to Buy". Retrieved March 11, 2013. - ↑
Guttenberg, Steve (July 16, 2009).
“Are SACD and DVD-Audio already dead?” . CNET
. Retrieved March 11, 2013. - ^ abcdefg Extremetech.com, Leslie Shapiro, July 2, 2001. Surround Sound:
High-End: SACD and DVD-Audio. "SACD stereo recording has a data rate of 5.6 Mbit/s, which is four times the stereo CD data rate of 1.4 Mbit/s." Retrieved May 20, 2009. - ↑
PC Magazine Encyclopedia Definition of Hybrid SACD, retrieved June 16, 2009. - ^ abc Middleton, Chris; Zook, Allen (2003). The Complete Guide to Digital Audio: A Comprehensive Introduction to Digital Audio and Music Production. Cengage Learning. paragraph 54. ISBN 978-1592001026.
- Clifford, Martin (1987). "Complete CD Player." Prentice Hall. paragraph 57. ISBN 0-13-159294-7.
- How Hybrid Super Audio Compact Disc (SACD) Works “SACD players are equipped with optical sensors that emit laser light at 650 nm, which is reflected by the DSD layer. However, the optical sensors in all CD players emit laser light at a wavelength of 780 nanometers, which is transparent to the DSD layer, so only the CD layer is readable." Retrieved June 16, 2009
- Rifman, Derk; Nuijten, Peter. "Why Direct Stream Digital is the best choice for digital audio format." (PDF) Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper 5396, May 2001.
- Ambisonic.net. Richard Helen, August 2001. Battle of the Discs. Retrieved May 20, 2009.
- Practical-home-theater-guide.com Direct Stream Digital Technology Retrieved June 3, 2009
- ISO/IEC (2006-03-14). "ISO/IEC 14496-3:2001/Amd 6:2005 – Lossless oversampling audio coding". ISO. Retrieved October 9, 2009.
- ISO/IEC (2007-08-06). "ISO/IEC 14496-4:2004/Amd 15:2007 – Lossless encoding of oversampled audio". ISO. Retrieved October 9, 2009.
- ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11/N6674 (July 2004), ISO/IEC 14496-3:2001/FPDAM6 (lossless oversampled audio coding). (DOC), retrieved October 9, 2009.
- ↑
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG 11 N7465 (July 2005). "Description Lossless Encoding of Oversampled Audio". chiariglione.org. Retrieved October 9, 2009. - ↑
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG 11 N7465 (July 2005). "Description Lossless Encoding of Oversampled Audio". Archived from the original on 2007-02-03. Retrieved December 28, 2009. - ISO/IEC (2009-09-01), ISO/IEC 14496-3:2009 - Information technology - Audiovisual object coding - Part 3: Audio (PDF), IEC, retrieved 10/07/2009
- ISO/IEC (2007), ISO/IEC 14496-5:2001/Amd.10:2007 - Information technology - Audiovisual object coding - Part 5: Reference software - Amendment 10: SSC, DST, ALS and SLS reference software ( ZIP), ISO, received 10/07/2009
- ISO/IEC (2007-03-01), ISO/IEC 14496-5:2001/Amd.10:2007 - SSC, DST, ALS and SLS reference software, ISO, retrieved 2009-10-09
- "Sony launches hybrid super audio CDs in Europe". SA-CD.net. 2003-01-22. Retrieved July 12, 2007.
- "Details on DVD-Audio and SACD". DVDdemystified.com. Retrieved July 12, 2007.
- "Sakd the Ripper".
- Fries, Bruce; Marty Frees (2005). Digital Audio Basics. O'Reilly Media. paragraph 147. ISBN 978-0-596-00856-7.
- "24/192 Music Downloads...and Why They Make No Sense". Archived from the original on 04/26/2020: “When using figure dithering... the effective dynamic range of 16-bit audio reaches 120 dB in practice.”
- ^ ab Rossing, Thomas (2007). Springer Handbook of Acoustics. Springer. pp. 747, 748. ISBN 978-0387304465.
- Galo, Gary (2008). “Is SACD Doomed?” (PDF). Audioxpress.com. Retrieved February 11, 2022.
- ^ a b E. Brad Meyer and David R. Moran (September 2007). "Audibility of a CD-standard A/D/Analog loop inserted during high-resolution audio playback" (PDF). J. Audio Eng. Soc
.
Audio Engineering Society. 55
(9): 775–779 - via drewdaniels.com. - ↑
Paul D. Lehrman: The Emperor's New Sampling Rate
Mix
online, April 2008 - "Audibility of a CD-standard A/D circuit inserted during high-resolution audio playback" (PDF). J. Audio Eng. Soc. Retrieved March 24, 2015.
- Reiss, Joshua D. (2016-06-27). "Meta-analysis of high-resolution audio perception assessment". Journal of the Audio Engineering Society
.
J. Audio Eng. Soc. 64
(6):364–379. DOI: 10.17743/jaes.2016.0015. - Blech, Dominikp; Yang, Ming-Chi. "DVD-Audio vs. SACD: Perceptions of Discrimination among Digital Audio Encoding Formats." (PDF) Audio Engineering Society Convention 6086, May 2004.
- "1-Bit Advantage - Future Write" (PDF). Korg. Retrieved December 31, 2011.
- Toshiyuki Nishiguchi, Kimio Hamasaki, Masakaz Iwaki and Akio Ando, “Perceptual Discrimination of Musical Sounds with and without Very High Frequency Components” [5] Published by NHK Laboratories in 2004
- Marui, A., Kamekawa, T., Endo, K., & Sato, E. (2014, April). Subjective evaluation of high-resolution recordings in PCM and DSD audio formats. In Convention 136. Audio Engineering Society.
- "Sony SCD-1 SACD player". @udiophilia. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- Onkyo's list of CD players lists one SACD player, the C-S5VL. Retrieved March 21, 2012
- Denon's web page shows one SACD player, the DCD-SA1. Retrieved June 3, 2009
- The Marantz Hi-Fi components list shows one SACD player, and the Marantz "Reference series" list shows four SACD players. Retrieved June 3, 2009
- PD-D6-J and PD-D9-J are two SACD players, Pioneer. Retrieved June 3, 2009
- Yamaha's web page shows the CD-S1000 and CD-S2000 SACD players. Retrieved June 3, 2009
- "Sony Announces Three Super Audio CD Car Stereo Players". High precision review. Archived from the original on 2007-03-02. Retrieved January 18, 2007.
- Practical-home-theater-guide.com SACD Playback and Content Protection Requirements "SACD compatible players are not permitted to transmit DSD digital content over an unencrypted digital audio link" retrieved June 18, 2009
- "Why did Sony remove SA-CD from PS3 again?" . PS3 SACD FAQ. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- "Firmware v2.01". PS3SACD.com. November 22, 2007. Retrieved August 11, 2010.
- "Blu-ray Disc Players Compatible with Super Audio CD". Retrieved October 21, 2009.
- Maxim V. Anisyutkin. "Super Audio CD Decoder". SourceForge. Retrieved March 18, 2012.
- "Audirvana Plus". Audirvana. Retrieved November 26, 2013.
SACD: Format information
Super Audio Compact Disk (SACD) is a digital audio recording format also developed by audio industry giants Sony and Philips. The official appearance of the new standard was made public in 1999. The size of the disc remains the same, but only the working layer is now golden, there are two layers in total. The duration of the sound has also been increased, compared to the CD - 74 and 109 minutes. Typically, audio is recorded in SACD format on one layer of a hybrid disc, and in Audio-CD format on another layer.
Discs can be listened to even on regular Audio-CD players, but SACD players use Multi Channel sound (multi-channel) , also known as Surround. Sometimes stereo sound is recorded, but very rarely, just like mono. Recording in mono and stereo modes is used mainly for re-releasing old albums and recordings.
SACD: Advantages of the standard
- 1. Natural sound
- 2. Copy protection
- 3. Multi-channel audio (up to six channels)
SACD: tech. information about the standard
The ability to record a disc of longer duration was realized due to a radically new technology for compression and encoding of the audio signal, as well as due to the physical reduction of pits (cell sizes) on the working surface of the disc. New Direct Stream Digital (DSD) technology is used to digitize the audio signal, which is converted into digital form using an ultra-high sampling rate (2822 kHz). Compared to a regular CD, the conversion quality is much higher and very close to the analog original. This is achieved due to the high frequency of data reading. This format uses the Direct Stream Transfer algorithm (lossless compression). The volume of the digital stream is almost halved.
The SACD audio signal has a frequency band of up to 96 kHz, versus 20 kHz on a regular CD, and a dynamic range of 144 dB, versus 96 dB on a CD. The sampling frequency is 2822.4 kHz.
Copy protection
The SACD standard has unique copy protection . The disk has special secret sectors that contain information about the disk, its manufacturer, and also contains a code key. The latter is read by the player before playback starts. If a disc is overwritten, it will have missing sectors and will not play. The disk data is also encrypted using a key. PSP tags can only be copied by a licensed SACD burner. Also, on all SACD playback devices, a “plug” is used on the digital output to prevent signal capture from the outside.
Since 2010, DSD audio files with the DSF or DSDIFF extension began to appear on the Internet. Using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and special software, these files can be played on a PC, and they can also be converted into files in the following formats: WAV, WMA, MP3, OGG, APE, FLAC.
A DSD disc is (DVD-R, DVD+RW, DVD+R, DVD-RW) an optical disc with DSD files with the DSF extension, which can be played on a PC and other devices that support this format. The quality of audio recording on this disc is identical to SACD, but a multi-channel signal cannot be recorded on a DSD disc.
Contents [edit]
Main article: List of SACD artists
By October 2009, record labels had released over 6,000 SACD releases, just over half of which were classical music. The next two most numerous genres were jazz and popular music albums, mostly remastered previous releases. [9] [10]
Many popular artists have released part or all of their back catalog on SACD. The Dark Side of the Moon had sold over 800,000 copies by June 2004
(1973) in SACD Surround Sound version.
[11] The Who's rock operas Tommy
(1969), and Roxy Music's
Avalon
(1982), were released on SACD to take advantage of the format's multi-channel capabilities. All three albums were remixed in 5.1 surround and released as hybrid SACDs with a stereo mix on a standard CD layer.
Some popular artists have released new recordings on SACD. Sales figures for Sting's Sacred Love
(2003) album reached number one on the SACD sales charts in four European countries in June 2004 [11]
Between 2007 and 2008, the rock band Genesis re-released all of their studio albums in three box sets. Each album in these sets contains the album on SACD in both new stereo and a 5.1 mix. There were no original stereo mixes on the disc. The US and Canadian versions use CD rather than SACD.
By August 2009, 443 labels[12] had released one or more SACDs. Rather than relying on major label support, some orchestras and artists are releasing SACDs themselves. For example, the Chicago Symphony Orchestra founded the Chicago Resound label to provide full and growing support for high-resolution SACD hybrid discs [13], and the London Symphony Orchestra founded its own label, LSO Live. [14]
Many SACDs released between 2000 and 2005 are now out of print and are only available on the used market. [8] [15] By 2009, major record labels had stopped regularly releasing discs in this format, and new releases were limited to smaller labels. [16]
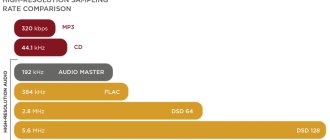
Let's sum it up
For greater clarity, we will collect all our technical characteristics that were mentioned in this article. Also, for clarity, the minimum cost of players capable of using most of the capabilities of the corresponding format has been added to the table.
| CD | DVD-Audio | SACD | |
| Permission | 16 bit PCM | 16-, 20-, 24-bit PCM | 1 bit DSD |
| Sampling frequency | 44.1 kHz | 44.1-192 kHz | 2.8224 MHz |
| Dynamic range | 96 dB | 144 dB (theoretically) | 120 dB |
| frequency range | 20—20,000 Hz | 5 – 96000 Hz | 20—50,000 Hz |
| Disk capacity | 700 MB | 4.7—8.5 GB | 4.7—8.5 GB |
| Playing time | 80 min. | >120 / 109 min. | |
| Stereo | + | + | + |
| Surround Sound | – | 5.1 (except 192 kHz) | 5.1 |
| Minimum cost of the player according to Yandex Market as of July 15, 2013 | Tangent CDP-200 – from $126 | (A model with 5.1CH audio was selected) OPPO BDP – 103 – from $1258 | (A model with 5.1CH audio was selected) NAD M5 – from $1,774* The first two versions of the PlayStation 3 (until 2007.10) fully reproduce SACD. |
Sound formats DVD-Audio, SACD, CD-Audio have changed this world, what will happen next - time will tell!