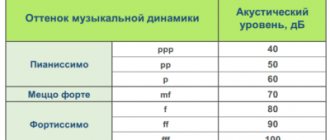
Probably every computer owner has used it at least once to listen to music, watch movies, perhaps talk with loved ones, or even record himself singing. This opportunity has become such a part of a computer user’s life that he doesn’t even think about how it all happens. What a sound card is, without which a computer cannot function properly, will be discussed in this article.
How it works?
Most sound cards use a DAC (Digital to Analog Converter) to convert digital audio signals to analog. The signal is output to conventional headphones and other acoustic devices. More advanced cards may include more than one sound chip to support high data rates and perform multiple simultaneous functions.
Characteristics
When it comes time to choose an interface, there is a risk of getting confused about the characteristics. Among them, there are basic qualities that you should first pay attention to when purchasing. You need to compare your tasks with these characteristics.
- Number of connectors (I/O) and types of connections with other devices
- Method of connecting to a computer/tablet
- External DSP processing
- Equipment
- Sound quality
- Budget
Inputs and outputs
This is one of the main parameters when purchasing. At the basic level there are interfaces with two channels, with which you can simultaneously record two audio signals in mono or one in stereo. From such cards the functionality can grow to expensive systems that can convert into “digital” and receive signals from dozens of channels simultaneously. Decide what you need to write down now and in the near future.
For example, if you are a songwriter who uses the card for voice and acoustic guitar, two mic inputs will be sufficient. If both microphones are condenser, there should be phantom power at each input. To record several people with the instrument, you will already need an interface with four inputs.
If you play bass, electric guitar, or keyboards, you'll want to have a direct way to connect to the card. You will need a hi-Z input - a signal of the appropriate level is transmitted through this connector.
External equipment such as drum machines, samplers, and effects processors require line-level jacks. You will need them when you connect studio monitors and headphone preamps to the interface.
Some devices require digital connectors. The most common are S/PDIF and ADAT, through which multi-channel microphone preamplifiers are connected to the audio interface. This way you can record more sound sources at the same time or free up the standard analog inputs. The interface with two or four mic preamps and an ADAT input can be expanded to ten or twelve inputs.
Before purchasing an audio interface, make a diagram of all the instruments and equipment you want to connect. Consider what equipment will need to be used at the same time.
Finally, pay attention to drivers and how they work with Windows or MacOS. Stability is the deciding factor.
Method of connecting to a computer
USB: The most common connection method. It is also convenient because many audio cards only need power via USB. USB 2.0 is gradually being replaced by the 3.0 standard. Please note that connector and bus are two different things! It happens that the device connector is already Type-C, and the bus operates according to the old 2.0 standard. iOS-compatible devices also connect via USB.
FireWire: Predominantly a Mac format that is slowly being replaced by Thunderbolt. The connector is fast and suitable for multi-channel recording.
Thunderbolt: New Apple computers are equipped with this bus. Owners also manage to install an expansion card. The format is characterized by a very high data packet transmission rate and ultra-low latency.
PCIe (PCI Express): an internal card of this format eventually occupied the niche of purely professional solutions for large studios, as well as users of the Avid ProTools ecosystem. Used in desktop computers, audio interfaces are installed as an additional board. PCIe offers high bandwidth and low latency. Cards usually have a large number of connectors. Probably not intended for a laptop.
External DSP processing
This means the presence of a separate chip, the power of which is entirely used for processing digital effects. The computer is significantly unloaded, which has a positive effect on the overall system performance. The chip comes with high-end plugins included, which are used as a serious studio tool.
Equipment
Please note what comes with the audio interface. Now the package is not limited to a computer cable. If the manufacturer has made sure that you have a full-fledged product with working software, you can save time and start projects. The package may include DAWs (and not only Lite versions), plugins, subscriptions to Splice services for collaborations, and access to discounts on virtual instruments.
Sound quality
Quality consists of the following characteristics:
DAC and ADC bit depth: the more bits, the higher the signal resolution. The numbers indicate how similar the recorded and digitized signal is to the original sound, what volume range is possible, and how effectively noise is suppressed.
The audio CD format uses a 16-bit standard with a dynamic (i.e. volume) range of 96 dB. Unfortunately, the level of background noise on a digital recording will be quite noticeable, so recording at 16-bit means that some noise will creep in during quiet sections of the recording.
24-bit recording is the standard in professional audio. The dynamic range here is 144 dB, and the noise level is almost completely leveled. From the listener's point of view, this means that the recording will sound smoother, brighter and cleaner.
DAC and ADC sampling frequency: the parameter indicates how many fragments the sound wave is divided into when converted to digital form. In CD format it is equal to 44.1 kHz - i.e. Every second, the audio signal is divided into 44,100 consecutive fragments. In theory, this means your system operates at frequencies up to 22.05 kHz, which exceeds the sensitivity of human ears. Commercial studios work with sampling rates of 48 kHz, 96 kHz and even 192 kHz.
How necessary is such permission? It depends on the goals. If you are recording a working demo of a track, then 16-bit/44.1 kHz will be sufficient. And for commercial releases and soundtracks, the standard is 24 bit/96 kHz.
Converter level: Converters are divided into ADCs (analog-to-digital converters, A/D) and DACs (digital-to-analog, D/A). The quality of sound depends no less on the quality of the converters and the careful assembly of card components than on the sampling frequency and bit depth. The correlation is somewhat rough, but nevertheless, the quality is reflected in the price. The better the converters, the more expensive the card.
Where is the sound card?
Regardless of the fact that a computer does not require a sound device to function, sound cards are included for the convenience of the user in most, either in an expansion slot, integrated into the motherboard, or connected through external ports.
Integrating a sound card into the motherboard allows for cheaper assemblies compared to an expansion card and with an imperceptible loss of sound quality for the average user. Separate sound cards, as practice shows, are only necessary for a serious audio professional or for use when the integrated one fails.
The sound card is installed into slots on a modern PCI or PCIe motherboard. A typical card has an interface that can be accessed on the rear panel with various audio output and input ports, and depending on the design of the computer case, audio input and output ports located on the sides of the case or even at the top.
For computers, the upgrade of which usually involves increasing the amount of RAM or replacing the hard drive with a solid-state drive (laptops, all-in-one PCs, nettops), it is possible to use an external sound device that performs the function of a sound card, usually connected to the computer via USB ports.
Types of cards
There are two types of audio cards - integrated and discrete. External ones are connected via FileWire or USB. Internal when assembling a computer by attaching expansion slots inside the system unit.
The main disadvantage of embedded devices is the huge risk of poor-quality PC power supply, that is, power surges and failure of the power supply. External ones are more practical, which is explained by external volume controls. Moreover, a unit of this type can work with both a laptop computer and a laptop or netbook.
In the case of an integrated card, its functions are performed by a processor that processes signals and converts sound. The discrete card has a personal sound processor, and some models even have their own memory.
So why do you need an external sound card if you have a built-in one? It's simple, with its help you can achieve the highest quality and clearest sound, as well as gain access to a number of important settings.
Drivers and software
Typically, the sound card or sound chip, in the case of integrated audio, comes with proprietary software on disk or can be downloaded from the hardware manufacturer's website. Modern operating systems can easily detect and load drivers for popular sound cards.
Such software can allow the user to make more subtle adjustments and provide recording, editing, etc. tools.
Maximum DAC frequency
The sampling rate of the DAC card that plays mp3 files must be 48 kHz or higher. Otherwise, the conversion result may differ from the original signal, and the sound will be distorted. Among lovers of the highest quality audio, there is a widespread opinion that the sampling frequency of lossless music should be even higher – 96 kHz. Buying a device equipped with a DAC with the same or higher frequency only makes sense if you will listen to similar tracks. If the maximum frequency of the DAC is higher than the actual frequency of the source, it will not improve the sound quality.
Why do you need a non-integrated audio card?
Devices with advanced functionality for music lovers can be equipped with a midi interface or SPDIF (Sony-Philips Digital Interface), input and output ports, headphone jacks with their own volume controls, the ability to connect to a computer not only via PCI and PCI-e, but also FireWire, USB, etc.
If the built-in sound card does not work
It just so happens, sometimes you may find that your computer has stopped playing your favorite music, there are no those fantastic sounds in your favorite game and movies have become deaf and dumb, like at the beginning of the last century. What could have happened?, you think. The drivers are installed, the volume controls are turned all the way up, but there is no sound.
The culprit of this event is the sound chip. The sound chip can be built into the motherboard or can be a separate board. Of course, you can go to a computer store and buy a new board. But we will try to repair our motherboard ourselves.
The built-in sound on my EPOX EP-8KDA7I motherboard stopped working.
First, let's check whether your speakers (headphones, stereo, etc.) are connected correctly. In the simplest case, look for the green connector for connecting speakers on your motherboard and see if you are connected here (
Fig. 1. )
Next, check for the presence of jumpers on the connector for connecting audio and microphone outputs to the front panel of the computer ( Fig. 2. )
We find the sound chip itself on the board ( Fig. 3. ) (we inspect the chip for thermal damage)
Near the sound chip there is usually a power stabilizer that “powers” our sound chip ( Fig. 4. ) (we also check that the stabilizer does not overheat, to do this you need to turn on the motherboard for a few seconds and carefully touch the stabilizer body with your finger, during normal operation the stabilizer heats up a little higher than ambient temperature and does not burn your finger)
We found out that the sound chip itself was faulty. In our case, this is a Realtek ALC655 chip ( Fig. 5. ).
Typically, audio repair involves resoldering this microcircuit.
In order to unsolder the microcircuit, I used a hot-air soldering station (popularly just a HAIRDRYER) from the Chinese company Lukey 852 ( Fig. 6. ).
Carefully shield (close) the plastic parts of the motherboard near the sound chip mixer circuit ( Fig. 7. ).
We apply soldering flux to the legs of the microcircuit ( Fig. 8. ).
Now you need to carefully desolder the microcircuit with a hairdryer ( Fig. 9. ).
Having soldered the microcircuit, we remove the remains of the burnt flux from the motherboard. We find an unnecessary motherboard with a working sound chip and remove the “donor” from it. We put the “donor” on our patient, add flux and solder the sound chip. We check the quality of soldering with a needle ( Fig. 10 ). (we run a needle along the legs of the chip, check that all the legs are soldered, also carefully inspect if there are any “sticky” legs, if necessary, carefully remove excess solder using a sharp soldering iron).
We remove the remaining flux from the soldered microcircuit (
Fig. 11_1. , Fig. 11_2. ).
Connect the motherboard and enjoy the sound. The renovation is ready.
DizzY
Colors of analog 3.5 mm sound card connectors
Most sound cards have ports for connecting speakers, microphones, and auxiliary devices. But there are also cards with more input and output ports designed for more advanced tasks.
Below are the most common audio connectors:
- Pink – microphone audio input;
- Light blue – linear audio input;
- Light green – linear audio output for the main stereo signal (front speakers or headphones);
- Orange – linear audio output for the center channel or subwoofer;
- Black – linear audio output for surround sound, usually the rear speakers;
- Gray – linear audio output for surround sound from side speakers.
There is also an additional gaming port - MIDI -15 pin connector for connecting additional audio devices.
What is important to consider before purchasing a device
The use of a more advanced system is required by all tasks that are in one way or another related to semi-professional sound processing - composing and recording music, vocals, multi-track sound recording, editing, digitizing recordings from analogue media. Most of these tasks require ASIO drivers on the computer.
To record vocals or a musical instrument, you need an amplifier, which is not always included in the built-in sound card. We are talking specifically about vocals: a voice message or podcast with a normal voice volume can be recorded on any audio device.
Also, in the absence of an amplifier, digitized recordings are usually of terrible quality, although in this case a lot depends on the source. It should also be taken into account that built-in sound cards are almost never equipped with a MIDI interface, which is necessary for connecting many instruments.
I would especially like to mention streamers and let-players who specialize in games. In the first case, the load on the computer increases: in addition to the fact that the game itself is running, the video and sound must be broadcast to a specialized resource. And in good quality, since their audience is very demanding in this regard.
When recording gameplay and further processing for the purpose of publishing on video hosting, another unpleasant surprise may lie in wait: the game worked without lags, but, for example, BandiCam or Fraps, recorded the process with “stutters”.
Dancing with a tambourine and fiddling with the settings of the video grabber and the game itself are usually useless: the reason is the insufficient power of the sound card, which can no longer record sound without delays.
But even if you are not a streamer or a Let's Play player, but just want to build a powerful gaming computer, having a good discrete sound card will not be superfluous.
Also worthy of attention are gentlemen music lovers and other audiophiles with expensive high-quality stereo systems. In order for the sound to be decent, you will need an appropriate sound system. Alas, sound quality is a subjective concept and cannot be measured .
In this case, many other factors should be taken into account: the size of the room, its shape, the location of the stereo system, etc., as well as the noise emitted by the computer itself. It is possible that in this case we will have to take care, among other things, to reduce it.
From the history
In the past, computers could produce signals using a narrow range of frequencies as warning signals. With the growth of multimedia comes the need for high quality audio for entertainment and professional reasons.
The Adlib sound card has become a pioneer in these areas. It provided a more natural sound than the Creative Music System released around the same time in 1988.
The introduction of Sound Blaster sound cards by Creative Labs greatly increased their capabilities, allowing digital audio recording and playback. Therefore, Sound Blaster can be called the first sound card that made digital audio possible.
This increase in functionality led to the multimedia evolution of computers and audio-enabled programs created for them. Audio quality continues to evolve in terms of hardware and software.
Modern audio cards can provide higher quality 3D surround sound output. Computer programs and games are developed to take full advantage of their capabilities and satisfy human needs.
Main types
Based on functionality, the devices under consideration are divided into two main types - professional and multimedia.
The first type is used for recording from microphones or musical instruments, voice acting and editing audio tracks.
Such devices are usually external and equipped with many controls and connectors. High demands are also placed on the ADCs and DACs built into them - they must output really high-quality sound. The disadvantages of this type of audio card include the high cost and general “tailoring” for professional activities - for example, they often do not have support for gaming surround sound technologies.
Multimedia sound cards are intended for home use and have a wide range of prices and technical characteristics. They often do not have specialized connectors, and adjustment is performed programmatically using the included software. Most devices of this type support gaming sound standards.
Summing up
This article covers the topic of the sound card, and repeatedly points out that the capabilities of the sound card and audio speakers, the entire audio system, affect the overall sound quality.
Many motherboards today have built-in sound cards, they are equipped with special chips, and the ports can be routed anywhere, depending on the design of the device. But you can use third-party sound cards and external audio devices, purchase and install them separately, although the capabilities of the built-in devices will probably be sufficient for people who are not sound fans.
- Forward
Comments
-6 profile 10.30.2018 21:31
Need cheap hosting? Try webhosting1st, just $10 for an year.
Reply Reply with quote Quote
Update list of comments
Add a comment
What is a sound card and what is it for?
What is an SSD? Solid State Drive
What is a processor, central processing unit, CPU?
What is a motherboard or system board and what is it used for?
What is HDD, hard drive and hard drive
What is RAM and Random Access Memory
Sound Features
Dolby Digital and DTS Digital Surround are surround sound standards used in the DVD format. If the PC is equipped with an audio card that supports the same standards, then the sound is reproduced without any distortion or noise, creating the effect of presence.
Today, the standards of audio devices for the highest quality reproduction of music and sounds are incredibly diverse. One of them, EAX and its improved version, EAX ADVANCED HD, guarantee excellent sound quality, which is achieved through the use of modern effects technologies.