In car audio, there are many options for acoustic design of boxes. Therefore, many beginners do not know what is the best choice. The most popular types of subwoofer boxes are a closed box and a bass reflex box.
There are also designs such as bandpass, quarter-wave resonator, freeair and others, but when building systems they are used extremely rarely for various reasons. The speaker owner must decide which subwoofer box to choose based on sound requirements and experience.
We advise you to pay attention to the article on what material is best to make a subwoofer box from. We have clearly demonstrated how the rigidity of the box affects the quality and volume of the bass.
Closed box
This type of design is the simplest. A closed box for a subwoofer is easy to calculate and assemble. Its design is a box of several walls, most often 6.
Advantages of ZY:
- Simple calculation;
- Easy assembly;
- Small displacement of the finished box, and therefore compact;
- Good impulsive characteristics;
- Fast and clear bass. Plays club tracks well.
A closed box has only one drawback, but sometimes it is decisive. This type of design has a very low level of efficiency compared to other boxes. A closed box is not suitable for those who want high sound pressure.
However, it is suitable for fans of rock, club music, jazz and the like. If a person wants bass, but needs space in the trunk, then a closed box is an ideal option. A closed box will not play well if the wrong volume is selected. What volume of box is needed for this type of design was long ago decided by experienced people in car audio through calculations and experiments. The choice of volume will depend on the size of the subwoofer speaker.
The most common speaker sizes are: 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 18 inches. But you can also find speakers of other sizes; as a rule, they are used very rarely in installations. Subwoofers with a diameter of 6 inches are produced by several companies and are also rarely found in installations. Mostly people choose speakers with a diameter of 8-18 inches. Some people indicate the diameter of the subwoofer speaker in centimeters, which is not entirely correct. In professional car audio, it is customary to express dimensions in inches.
Recommended volume for a closed box subwoofer:
- an 8-inch subwoofer (20 cm) requires 8-12 liters of net volume,
- for 10-inch (25 cm) 13-23 liters of net volume,
- for 12-inch (30 cm) 24-37 liters of net volume,
- for 15-inch (38 cm) 38-57 liters net volume
- and for 18 inches (46 cm) you will need 58-80 liters.
The volume is given approximately, since for each speaker you need to select a certain volume based on its characteristics. The setting of a closed box will depend on its volume. The larger the volume of the box, the lower the tuning frequency of the box will be, the bass will be softer. The smaller the volume of the box, the higher the frequency of the box, and the bass will be clearer and faster. You should not increase or decrease the volume too much, as this is fraught with consequences. When calculating the box, adhere to the volume that was indicated above. If there is too much volume, the bass will turn out vague and indistinct. If the volume is not enough, then the bass will be very fast and “pound” the ears in the worst sense of the word.
A lot depends on how the box is configured, but an equally important point is “Setting up the radio.”
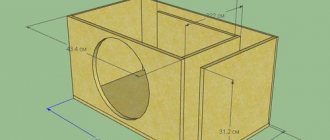
Box for 2 Molot 12 speakers with 40Hz port setting
Box detailing
The small number and simple shape of the subwoofer housing parts allow them to be made in a home workshop or ordered from any furniture factory. In the first case, you can be proud of your skills, and in the second, you will save time and nerves. It should be immediately noted that the most important parameter that should be paid attention to is the solidity, structural strength and tightness of all connections of the subwoofer; this is much more important than appearance.
The dimensions of the parts are as follows:
| № | the name of detail | Dimensions(MM) | PC |
| 1 | Right wall | 365 x 403 | 1 |
| 2 | Back wall | 365 x 868 | 1 |
| 3 | Left wall | 365 x 385 | 1 |
| 4 | Front wall | 365 x 768 | 1 |
| 5 | Bass reflex wall 1 | 365 x 303 | 1 |
| 6 | Bass reflex wall 2 | 365 x 251 | 1 |
| 7 | Rounds (Both sides at 45° angle) | 365 x 72 | 3 |
| 8 | Fillet (One side at 45° angle) | 365 x 72 | 1 |
| 9 | Lid and bottom | 868 x 421 | 2 |
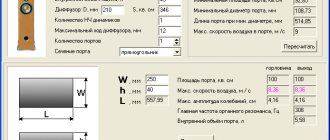
Box characteristics
| 1 | Subwoofer speaker | Ural Molot 12 |
| 2 | Port configuration | 40 Hz |
| 3 | Net volume | 90 l |
| 4 | Overall volume | 146.5 l |
| 5 | Port area | 300 cm cube |
| 6 | Port length | 58.91 cm |
| 7 | Material thickness | 18 mm |
| 8 | Dimensions MM (L,W,H) | 421 x 868 x 401 |
| 9 | What body was calculated for? | Sedan |
Recommended amplifier settings for a box with 2 speakers
We understand that a large number of people visiting our portal are non-professionals, and they worry that if configured and used incorrectly, they can render the entire system unusable. To relieve you of your fears, we have made a table with recommended settings for this calculation. Find out what the power rating (RMS) of your amplifier is and set the settings according to the recommendations. I would like to note that the settings indicated in the table are not a panacea, and are only advisory in nature.
| Setting name | RMS 300 - 500w | RMS 500-700w | RMS 700-900w |
| 1. GAIN (lvl) | 85 — 75 % | 75 — 65 % | 65 — 40 % |
| 2. Subsonic | 28 Hz | 28 Hz | 29 Hz |
| 3. Bass Boost | from 0 to 50% | from 0 to 30% | from 0 to 15% |
| 4.LPF | 50 - 100hz | 50 - 100hz | 50 - 100hz |
*PHASE – smooth phase adjustment. There is such an effect as a temporary lag of the subwoofer bass from the rest of the music. However, by adjusting the phase this phenomenon can be reduced.
Before installing the amplifier, read the instructions, in it you will find what cross-section of the power wire is necessary for stable operation of your amplifier, use only copper wires, monitor the reliability of the contacts, as well as the voltage of the on-board network. Here we have described in detail how to connect the amplifier.
Frequency response of the box
Frequency response – graph of amplitude-frequency response. It clearly demonstrates the dependence of loudness (dB) on sound frequency (Hz). From which you can imagine how our calculation will sound when installed in a sedan car.
Bass reflex
This type of design is quite more difficult to calculate and build. Its design is significantly different from a closed box. However, it has advantages, namely:
- High level of efficiency. A bass reflex will produce low frequencies much louder than a closed box;
- Simple calculation of the body;
- Reconfiguration if necessary. This is especially important for beginners;
- Good speaker cooling.
The bass reflex also has disadvantages, the number of which is greater than that of the ZYa. So, the cons:
- FI is louder than ZY, but the bass here is not so clear and fast;
- The dimensions of the FI box are much larger compared to the ZY;
- Large displacement. Because of this, the finished box will take up more space in the trunk.
Based on the advantages and disadvantages, you can understand where FI boxes are used. Most often they are used in installations where loud and pronounced bass is needed. The bass reflex is suitable for listeners of any rap, electronic and club music. It is also suitable for those who do not need free space in the trunk, since the box will occupy almost all the space.
The FI box will help you get more bass than from a small-diameter speaker. However, this will require much more space.
What volume of box is required for a bass reflex?
- for a subwoofer with a diameter of 8 inches (20 cm) you will need 20-33 liters of net volume;
- for a 10-inch speaker (25 cm) – 34-46 liters,
- for 12-inch (30 cm) – 47-78 liters,
- for 15-inch (38 cm) – 79-120 liters
- and for an 18-inch subwoofer (46 cm) you need 120-170 liters.
Subwoofer volume
How to find out and calculate the volume of a subwoofer in liters. The most labor-intensive calculations will be for structures with a bass reflex or bandpass. Despite the high user parameters, the bandpass design is rarely used in cars. Calculation and production of an acoustic system with a slot bass reflex requires more parts and carpentry work. It is necessary to accurately calculate the area of the bass reflex port, and after manufacturing and assembling the structure, all internal corners must be carefully rounded to avoid air vortex waves. It’s easier to calculate a box for a subwoofer on a pipe.
The pipe is made of plastic and consists of two segments, one of which can move inside the other. Such a device is sold in specialized stores. The movement of the pipe components changes the effective area of the bass reflex, which allows you to tune the structure to a specific frequency.
Which box to choose for a subwoofer is determined by the type of speaker and location of the bass speaker. If the luggage compartment is empty and not used for transporting cargo, then it is best to place a low-frequency speaker system there. If part of the trunk is needed for any purpose, then it is better to choose a closed box, since it has minimal dimensions. When the trunk cannot be used, the bass speaker is mounted on a shelf behind the backs of the rear seats. In this case, the “Free Air” design is selected.
What types of subwoofer boxes are there?
There are several types of subwoofer boxes. you get at the output directly depends on the design of the box Below are the most popular types of subwoofers:
A closed box is the easiest to manufacture and design; its name speaks for itself. The woofer is housed in a sealed wooden housing, which improves its acoustic performance. Making a subwoofer in a car with such a housing is quite simple, but it has the lowest efficiency.
A 4th order bandpass is a type of subwoofer whose body is divided into chambers. The volumes of these chambers are different; in one of them there is a speaker, and in the second there is a bass reflex (air duct). One of the features of this type of subwoofer is the design's ability to limit the frequencies that the cone reproduces.
The 6th order bandpass differs from the 4th order by the presence of another bass reflex and another camera. There are two types of 6th order bandpasses - the first has one bass reflex, and the second has two (one of them is common to both cameras). This type of box is the most difficult to design, but produces maximum efficiency.
A bass reflex is a subwoofer with a special tube in the housing. It vents air and provides additional sound from the rear of the speaker. In terms of complexity in manufacturing and sound quality, this type is a cross between a closed box and a bandpass.
If you want to get the highest quality sound, you can opt for bandpasses. But this type of design has many details that must be carefully designed and calculated. All this can be done using a special program WinlSD, which will not only determine the optimal size and volume of the subwoofer, but also create a 3D model of it, and also calculate the dimensions of all parts.
Unfortunately, this program requires at least minimal knowledge in this area and the average car enthusiast is unlikely to be able to do everything right the first time. Moreover, in order for the program to work correctly, it needs some speaker parameters, which are also not known to everyone. If you do not plan to take part in car audio competitions, we advise you to discard the bandpasses.
Are you interested in auto tuning? Detailed instructions for installing parking sensors with your own hands especially for you!
How to calculate and calculate the volume of a subwoofer enclosure
A bandpass or bandpass system is an acoustic high- and low-pass filter. The design comes in fourth and sixth order. The acoustic low-frequency system consists of two sections, each of which is equipped with a bass reflex. The sections are divided into two volumes by a partition on which a loudspeaker is installed. The front and rear planes of the diffuser operate in their own space. A speaker with two volumes and one bass reflex is a fourth-order bandpass, and a system with two bass reflexes is a sixth-order bandpass. Calculating the box for a subwoofer of a bandpass system will be the most difficult. When calculating the displacement of a subwoofer, not only the size of the speaker is taken into account, but also the cutoff frequencies of the acoustic filters.
What materials do we need to assemble the subwoofer?
The material for making the subwoofer box must be durable, dense and well insulating sound. Multilayer plywood or chipboard is perfect for this . The main advantages of these materials are their affordable price and ease of processing. They are quite durable and provide good sound insulation. We will make a subwoofer from 30 mm thick multilayer plywood.
To make a subwoofer box we will need:
- Wood screws (approximately 50-55 mm, 100 pieces)
- Soundproofing material (Shumka)
- Drill and screwdriver (or screwdriver)
- Jigsaw
- Liquid Nails
- Sealant
- PVA glue
- Carpet, approximately 3 meters
- Klemnik
Assembling a subwoofer box with your own hands
You can start assembling. We use a 12-inch Lanzar VW-124 speaker.
Its diameter is 30 cm, and the first thing you need to do is cut a hole for the speaker. The minimum distance from the center of the diffuser to the subwoofer wall is 20 cm. We measured 23 cm (20 cm + 3 cm plywood width) from the edge of the panel and cut a hole with a jigsaw. Next, we cut a hole for the bass reflex slot; in our example, it has a size of 35*5 cm.
Instead of a slot, you can use a classic air duct - a tube. Now we assemble the bass reflex slot and attach it to the front panel of the subwoofer. We go along the joints with liquid nails and tighten them with self-tapping screws.
Next, we assemble the side walls of the box, having previously lubricated them with liquid nails, and tighten them tightly with self-tapping screws.
On the back cover of the box you need to cut a small hole for the terminal block. We connect all parts of the body. We make sure that we cut and fastened all the parts correctly.
We insert the speaker. Let's look and admire.
Let's move on to the interior decoration of the box. The first thing you need to do is seal all the joints and cracks with epoxy glue or sealant. Next, using PVA glue, we glue soundproofing material onto the entire inner surface of the box.
Now we cover the entire outer plane of the box with carpet, including the bass reflex slot. You can attach it with epoxy glue or using a furniture stapler.
Next, insert and screw the speaker tightly. The subwoofer is almost ready, all that remains is to stretch the wires from the speaker to the terminal block and connect the amplifier.
We bought an additional amplifier, but you can also make it yourself. This is quite difficult, as it requires knowledge and practice in the field of radio engineering. You can also use ready-made kits and circuits for radio amateurs, like Master-KIT, and assemble the amplifier yourself. The only requirement for the amplifier is that its maximum power must be less than the maximum power of the speaker .
See also a video report on making a homemade subwoofer for 2 speakers
Making Speaker Cabinets: Review of Materials
Professional active acoustics Denon DN-304S
Previously, speakers were ordinary horn loudspeakers and did not have a housing as such. Everything changed when speakers with paper cones appeared in the 20s of the 20th century.
Manufacturers began making large cases that housed all the electronics. However, until the 50s, many audio equipment manufacturers did not completely close the speaker cabinets - the back remained open. This was due to the need to cool the electronic components of that time (tube equipment).
The purpose of a speaker enclosure is to control the acoustic environment and contain the speakers and other system components. Even then it was noticed that the housing can have a serious impact on the sound of the loudspeaker. Since the front and rear parts of the speaker emit sound with different phases, amplification or attenuation interference occurred, resulting in deterioration of the sound and the appearance of comb filtering effect.
In this regard, the search began for ways to improve sound quality. To achieve this, many began to explore the natural acoustic properties of various materials suitable for the manufacture of enclosures.
Waves reflected from the inner surface of the walls of the speaker housing are superimposed on the main signal and create distortion, the intensity of which depends on the density of the materials used. In this regard, it often turns out that the case costs much more than the components contained in it.
When producing cabinets in large factories, all decisions regarding the choice of shape and thickness of materials are made on the basis of calculations and tests, but Yuri Fomin, a sound engineer and speaker design engineer, whose developments form the basis of multimedia systems under the Defender, Jetbalance and Arslab brands, does not excludes that even in the absence of special musical knowledge and extensive experience in the audio industry, it is possible to make something close in characteristics to “serious” Hi-Fi.
“We need to take ready-made developments that engineers share online and repeat them. This is 90% success,” notes Yuri Fomin.
When creating a speaker system housing, you should remember that, ideally, sound should come only from the speakers and special technological holes in the housing (bass reflex, transmission line) - you need to take care that it does not penetrate through the walls of the speakers. To do this, it is recommended to make them from dense materials with a high level of internal sound absorption. Here are some examples of what you can use to build a speaker enclosure.
Chipboard (chipboard)
These are boards made from compressed wood chips and glue.
The material has a smooth surface and a loose, loose core. Chipboard dampens vibrations well, but transmits sound through itself. The boards are easily held together with wood glue or assembly adhesive, but their edges tend to crumble, which makes working with the material a little more difficult. It is also afraid of moisture - if production processes are disrupted, it easily absorbs it and swells. Stores sell boards of different thicknesses: 10, 12, 16, 19, 22 mm and so on. For small cases (volume less than 10 liters) chipboard with a thickness of 16 mm is suitable, and for larger cases you should choose boards with a thickness of 19 mm. Chipboard can be covered: covered with film or fabric, puttied and painted.
Chipboard is used to create the Denon DN-304S speaker system (pictured above). The manufacturer chose chipboard because this material is acoustically inert: the speakers do not resonate or color the sound even at high volumes.
Lined with chipboard
This is chipboard, lined with decorative plastics or veneer on one or both sides. Boards with wood cladding are held together with regular wood glue, but for chipboard lined with plastic, you will have to buy special glue. You can use edge tape to process board cuts.
Joiner board
A popular building material made from slats, bars or other fillers, which are covered on both sides with veneer or plywood. The advantages of wood board: relatively light weight and ease of edge processing.
Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
OSB is boards pressed from several layers of thin plywood and glue, the pattern on the surface of which resembles a mosaic of yellow and brown colors.
The surface of the material itself is uneven, but it can be sanded and varnished, since the texture of the wood gives this material an unusual appearance. This slab has a high sound absorption coefficient and is resistant to vibrations. It is also worth noting that, due to its properties, OSB is used to form acoustic screens. Screens are necessary to create listening rooms where users can evaluate the sound of loudspeaker systems under near-ideal conditions. OSB strips are attached at a certain distance from each other, thereby forming a Schroeder panel. The essence of the solution is that a strip fixed at certain points, under the influence of an acoustic wave of the calculated length, begins to emit in antiphase and dampens it.
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF)
Made from wood chips and glue, this material is smoother than OSB.
Due to its structure, MDF is well suited for the manufacture of designer cabinets, since it can be easily cut - this simplifies the joining of parts fastened together using mounting adhesive. MDF can be veneered, puttied and painted. The thickness of the boards varies from 10 to 22 mm: for speaker bodies with a volume of up to 3 liters, a board with a thickness of 10 mm will be sufficient, for up to 10 liters - 16 mm. For large cases, it is better to choose 19 mm.
If, when choosing a material for the manufacture of speaker cabinets, we put aside the sound aspects, then three defining parameters remain: low cost, ease of processing, ease of gluing. MDF has all three. It is the low cost and “pliability” of MDF that make it one of the most popular materials for making speakers.
An example of using MDF is the Arslab Classic 1 SE bookshelf acoustics, the walls of which are made of thick wood-fiber boards that prevent vibrations and coloration of sound.
Plywood
This material is made from compressed and glued thin veneer (about 1 mm).
To increase the strength of plywood, veneer layers are applied so that the wood fibers are directed perpendicular to the fibers of the previous sheet. Plywood is the best material for suppressing vibrations and keeping sound inside the cabinet. You can glue plywood boards together with regular wood glue. Sanding plywood is more difficult than MDF, so you need to cut out the parts as accurately as possible. Among the advantages of plywood, it is worth highlighting its lightness. For this reason, it is often used to make cases for musical instruments, because it is quite a shame to cancel a concert because a musician injured his back.
It is this material that Penaudio uses to produce floor-standing acoustics - it uses Latvian plywood, which is made from birch. Many people like the way treated birch plywood looks, especially after varnishing - it gives the body a unique look. The company takes advantage of this: the transverse layers of plywood have become a kind of “calling card” of Penaudio.
Floor-standing speakers Penaudio Rebel Three
Stone
The most commonly used stones are marble, granite and slate.
Slate is the most suitable material for making cabinets: it is easy to work with due to its structure and it absorbs vibrations effectively. The main disadvantage is that special tools and stone processing skills are required. To somehow simplify the work, it may make sense to make only the front panel from stone. It is worth noting that to install stone speakers on a shelf, you may need a mini-crane, and the shelves themselves must be strong enough: the weight of a stone audio speaker reaches 54 kg (for comparison, an OSB speaker weighs about 6 kilograms). Such enclosures seriously improve sound quality, but their cost can be prohibitive.
The speakers are made from a single piece of stone by the guys from Audiomasons. The bodies are carved from limestone and weigh about 18 kilograms. According to the developers, the sound of their product will appeal to even the most sophisticated music lovers.
Plexiglass/glass
You can make a speaker housing out of transparent material - it's really cool when you can see the "insides" of the speaker.
Only here it is important to remember that without proper insulation the sound will be terrible. On the other hand, if you add a layer of sound-absorbing material, the transparent case will no longer be transparent. A good example of high-end acoustic equipment made from glass is the Crystal Cable Arabesque. Cases of Crystal Cable equipment are made in Germany from strips of glass 19 mm thick with polished edges. The parts are fastened together with invisible glue in a vacuum installation to avoid the appearance of air bubbles.
At CES 2010, held in Las Vegas, the updated Arabesque won all three awards in the field of Innovation. “Until now, no equipment manufacturer has been able to achieve true hi-end sound from acoustics made from such a complex material. – wrote the critics. “Crystal Cable has proven that it can be done.”
Laminated timber/wood
Wood makes good cabinets, but there is an important point to consider here: wood has the ability to “breathe”, that is, it expands if the air is humid and contracts if the air is dry.
Since the wooden block is glued on all sides, tension is created in it, which can lead to cracking of the wood. In this case, the housing will lose its acoustic properties.
Metal
Most often, aluminum is used for these purposes, or more precisely, its alloys.
They are light and tough. According to a number of experts, aluminum can reduce resonance and improve the transmission of high frequencies in the sound spectrum. All these qualities contribute to the growing interest in aluminum from audio equipment manufacturers, and it is used for the manufacture of all-weather speaker systems. There is an opinion that making an all-metal case is not a good idea. However, it is worth trying to make the top and bottom panels, as well as the stiffening partitions, from aluminum.
Our
Making a stealth subwoofer with your own hands
Tired of carrying a huge box in your trunk? Then the stealth subwoofer is just made for you. This unique type of case is more practical than the classic box. It doesn't sit in a square box in the middle of the trunk and takes up less space. Often, stealth is installed in the inner part of the wing, sometimes in a niche instead of a spare wheel. The minimum volume of the box that requires a 10-12 inch speaker for normal operation is 18 liters.
To make a passive stealth subwoofer we will need:
- subwoofer;
- protective grille and socket for connection to the amplifier;
- wire for connecting the speaker to the outlet;
- multilayer plywood or chipboard (thickness 20 mm);
- a small piece of fiberboard;
- epoxy adhesive;
- brush;
- fiberglass;
- mounting tape;
- polyethylene film;
- wood screws;
- drill, jigsaw.
Find out what documents are needed to replace your license when changing your last name, and whether you need to take your license again.
Have you recently bought a new car? Read tips on breaking in a new car from experienced motorists.
Here /avtotovary/pokupka-avto/byudzhetnye-krossovery.html you can learn how to properly use and care for an automatic transmission.
After choosing the place where the stealth will be installed, we empty the trunk and begin manufacturing the body. You can remove the trunk trim where the subwoofer will be installed to place it even closer to the fender. First of all, lay a plastic film on the floor of the trunk. It performs two functions at once: it protects the trunk lining from epoxy glue and allows us to make a mount to which we will screw the bottom of the subwoofer. Next, we cover the inside of the wing with mounting tape in two layers.
We cut the fiberglass into small pieces, approximately 20x20 cm. We place pieces of fiberglass onto masking tape and glue them with epoxy glue. It is better to overlap the fiberglass fabric so that there are no obvious joints and seams.
We sculpt layers of fiberglass on top of each other, simultaneously lubricating them with epoxy glue, until the thickness of the sheet reaches 10 mm (about 4-5 layers).
The material will harden in approximately 12 hours. To speed up the process, you can use a lamp. Now we cut out the bottom of the subwoofer and glue it to our body. The joint is treated with sealant or glued with epoxy resin.
In this particular case, the shape needs to be adjusted to the trunk hinges so that our homemade subwoofer does not interfere with its closing. After we cut off all the excess, we cut out the side walls and the top cover from chipboard. We make the rounded part from plywood, we did it “by eye”.
Box detailing
The size and number of parts for building the box, i.e. you can give the drawing to a company that provides wood cutting services (furniture), and after a certain time pick up the finished parts. Or you can save money and make the cut yourself. The dimensions of the parts are as follows:
We also have calculations for two Ural molot 12 subwoofers
Box characteristics
Frequency response box
This graph shows how the box will behave in a medium-sized sedan, but in practice small deviations are possible since each sedan has its own interior characteristics.
We are sure that you will be satisfied with the result, you can find a large number of answers to questions in the subwoofers section, and you can also ask us a question by filling out the form below. This will help us make our portal even better and more informational.
Sources used:
- https://caraudioinfo.ru/chertezhi/korob-dva-molot-12.html
- https://dinamikservis.ru/blog/sabvufery/podklyuchenie-saba-2×2-4×4-1-om/
- https://caraudioinfo.ru/chertezhi/korob-dlya-sabvufera-ural-molot-12-38hz.html
Subwoofer box
How you design your subwoofer is how it will sound. Of course, there are ready-made options - cabinet-mounted woofers, but you shouldn’t demand real performance and vibrations from them. This is the “middle”, designed for the average consumer, and is far from an audiophile and creative format.
The most popular types of acoustic design for low-frequency speakers are closed boxes and bass reflexes. A lot has been written about them, the advantages and disadvantages are described in detail, there are reviews, examples and much more.
The subwoofer box requires precise calculation; there is even a special program for calculating the volume of the subwoofer box. If you are faced with this issue for the first time, it is better to turn to professionals. Otherwise, the result will be disastrous: money down the drain and the lack of sound we are striving for.
What box volume is needed for a closed box?
- Subwoofer 8 inches - box 8-12 liters in its pure form
- Subwoofer 10 inches – box 13-23 liters
- Subwoofer 12 inches – box 24-37 liters
- Subwoofer 15 inches – box 38-57 liters
It is impossible to indicate the exact volume, since each woofer has its own characteristics and installation requirements; setting is also important here. If the volume of the box is larger than necessary, then the low frequencies will be blurry and not clear. If it is less, the bass will become “fast” and harsh, this is too much for human hearing.
What volume of box is needed for a bass reflex?
- Subwoofer 8 inches – 20-33 liters in pure form
- Subwoofer 10 inches – 34-46 liters
- Subwoofer 12 inches – 47-78 liters
- Subwoofer 15 inches – 79-120 liters
Unlike a closed box, a bass reflex enclosure can operate even at lower values, although here it is important not to overdo it. If the volume is too increased or decreased, you will not get sound; in the worst case, the result will be a loss of power and failure of the woofer.
Subwoofer with inverted speakers
Typically installed on demo cars for SPL competitions, where maximum sound pressure is particularly valued. Plus - savings in housing volume, the ability to install several subwoofers on one box. The speaker diffuser “pumps” volume in both directions. This is how SPL drivers achieve that very “wind” when everything around the cabin vibrates, including upholstery, long hair, and people. Such boxes are made by real professionals, relying on experience and knowledge in the subject of car audio.
Material requirements
Multilayer plywood, wood or chipboard are used as materials for the subwoofer box. You will also need sound insulation, sealant, screws, glue and tools. In the technical documents, each woofer comes with instructions indicating the required cabinet volumes for good sound. Drawings are developed in accordance with the box volumes recommended by manufacturers.
If you want to buy a box for a subwoofer, you can consult directly in the store; MVA specialists know a lot about this and will advise the required volume and type for the existing low-frequency speaker.
How to calculate the displacement of a subwoofer housing
To correctly determine the volume of a subwoofer enclosure, you need to take into account one important quantity. This is the transfer function of the car interior. It is defined very simply. You need to multiply the longest seat in the cabin by two and divide the speed of sound in air by this value. If the length is 2 m 45 cm, then the transfer function of the cabin will be equal to 343/4.9 = 70. The interior PFS is the frequency in hertz. This value is entered as a parameter when calculating the subwoofer box using computer programs.
The more parameters are entered into the speaker system design program, the more accurate and correct its volume will be calculated.