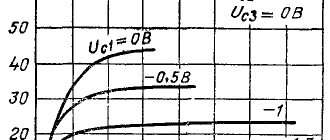According to the technical characteristics, 6N2P is a small electron tube, which is a double triode and has separate oxide cathodes, indirectly heated. Typically used in the pre-stages of a low frequency amplifier. It can work in any position. Until the mid-70s, it was often used in Soviet radios, receivers and televisions. The 6N2P-EV lamp was also produced with increased strength and durability, mainly for the military industry.
Tsokolevka
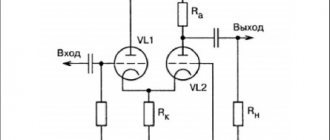
Let's disassemble the 6N2P pinout in a glass case with a pin base in which it was manufactured. Weight - up to 15 g, dimensions: length 56.5 mm, diameter 22.5 mm. Its appearance and location of the legs are shown in the figure below.
Here the numbers indicate:
- Anode of the 1st triode.
- Grid of the 1st triode.
- Cathode of the 1st triode.
4 and 5 heater.
- Anode of the 2nd triode.
- Grid of the 2nd triode.
- Cathode of the 2nd triode.
- Net.
Story
External view of the Eimac 750TL 750 W power triode.
Uranium glass was used at the exit point of the electrodes. To compare the size, below is an iron rectangle 10 cm long. Diagram of a vacuum triode with an indirectly heated cathode. Circuit designation of a vacuum triode with an indirectly heated cathode. Invented and patented in 1906 by the American Lee de Forest. Typically used to amplify, generate and convert electrical signals.
Name triode
in the 1950-1970s, during the formation of semiconductor electronics, it was also used for transistors - by the number of terminals, often with clarification:
semiconductor
triode, or indicating the material: (
germanium
triode,
silicon
triode).
Triodes were the first devices used to amplify electrical signals in the early 20th century.
The nonlinearity of the current-voltage characteristic of the triode is proportional to the square root of the third power of the anode current [1], that is, it has higher linearity than semiconductor transistors of the 20th century. Thanks to this, vacuum triodes introduce minimal nonlinear distortion into the amplified signal.
As the triode was further improved, multigrid lamps were developed: tetrode, beam tetrode, pentode and others.
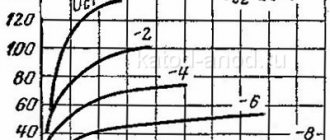
Technical characteristics 6N2P
- filament voltage (normal) – 6.3 V;
- filament voltage (maximum) – 7.0 V;
- filament voltage (minimum) – 5.7 V;
- current through the filament - 340 ± 25 mA;
- normal voltage at the lamp anode is 250 V;
- maximum voltage at the anode – 300 V;
- current through the anode – 2.3 ± 0.9 mA;
- maximum current through the cathode – 10 mA;
- grid voltage – -1.5 V;
- reverse current flowing through the triode grid – up to 0.2 μA;
- the maximum possible power of one triode is 1 W;
- the voltage between the cathode of the electron tube and its heater is 100 V;
- the voltage between the anodes of the vacuum tube is no more than 2 V;
- characteristics – 2.1 ± 0.5 V;
- maximum resistance in the grid circuit is 0.5 MΩ;
- lamp input capacitance – 2.35 ± 0.35 pF;
- durability – more than 5000 hours;
- storage time – more than 15 years;
- output capacitance of the 1st triode – 2.5 ± 0.5 pF;
- output capacitance of the 2nd triode – 2.5 ± 0.5 pF;
- pass-through capacitance – 0.7 ... 0.8 pF;
- capacitance between the anodes of the vacuum tube – no more than 0.15 pF;
- The capacitance measured between the cathode and the heater is no more than 5 pF.
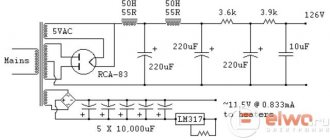
Amplifier power supply
The power supply is also not complicated. The anode voltage is rectified using a bridge and filtered by an RC filter consisting of resistors R101-R102 and capacitors C101-C107. Resistor R108 discharges high-voltage capacitors after turning off the power.
Resistors R105, R104 balance the filament voltage to ground, so the network noise heard in the speakers should be minimal. Resistor R101 gets quite hot, so for better heat dissipation it can be placed on a small radiator, or two can be connected at once - in series or in parallel (by selecting the resistance of individual resistors accordingly). This power supply provides power to both ULF channels simultaneously.
After switching on, the amplifier must warm up for several minutes so that the currents flowing through the lamps stabilize. Resistors R101 and R102 in the power supply, as well as R9 and R9A on the lamps, will heat up to a high temperature, this is normal. However, if there is a smell of scorched varnish in the air and we see that the paint on one of the resistors changes color, then the resistor has too little reserve. In this case, it should be replaced with one of the same rating, but with more power. After a longer period of operation, we again check the supply voltage and the voltage drop across the cathode resistors of the lamps. We correct the anode currents of lamp L2 (L2A).
Dual triodes
Double triode with common cathode.
Conventional graphic symbol. a1 is the anode of the first triode, a2 is the anode of the second triode, c1 is the grid of the first triode, c2 is the grid of the second triode, k is the cathode, n is the cathode heater. Double triode 6N2P (USSR) Combined lamps, structurally representing assemblies of two individual triodes enclosed in a common evacuated flask, are called double triodes
. Typically, both triodes have separate and isolated systems of electrodes - anodes, grids and cathodes. There are types of dual triodes with a common cathode. Almost always, the filament circuits of both cathodes are electrically connected inside the cylinder and only two filament leads are removed from the cylinder.
Basically, double triodes are devices designed to work in audio frequency amplifiers (ALF), industrial automation circuits, and switching circuits. But there are also high-frequency dual triodes, for example, 6N3P.
At the end of the lamp era, in order to increase the integration of lamp circuits, triple triodes were produced (compactron design), where three triodes were combined in one cylinder, but these lamps, unlike double triodes, did not become widespread. At that time In industry, the most widely used low-power double triodes were 6N2P, 6N1P, 12AX7, 6SN7, 6SL7, and others.
The use of dual triodes improved the weight and size characteristics of electronic equipment.
Domestic double triodes
Main article: Double electrovacuum triodes made in the USSR
- 1N3S
- double triode, low power with a common direct-heated cathode. Designed for use in ULF output stages (up to 1.5 W), operating in class B, which allows operation with battery power. - 6N5S
,
6N13S
- double low-frequency powerful triode, with an octal base, analogue of 6AS7. Designed for use in voltage stabilizers. Can be effectively used in high-quality ULFs; Most modern transformerless tube amplifiers are built on the basis of modern Russian-made 6N13S. - 6N7S
- double low-frequency triode with a common cathode, with an octal base, analogue of 6N7. Intended for differential stages of low-frequency amplifiers, as well as for final stages of ULF operating in class B. - 6N8S
- low-frequency double triode, with an octal base, analogue of 6SN7 - the most common lamp in modern equipment. Designed to amplify low frequency signals. - 6N9S
- low-frequency double triode with high gain, with an octal base, analogue of 6SL7.
After discontinuation of production, an analogue was produced in the 6N2P “finger” housing. Designed to amplify high[ specify
] frequency signals. It is used in television and transmitting and receiving equipment. - 6N1P
is a double miniature low-frequency triode, a functional analogue of 6N8S and 6DJ8. Features a higher filament current. Pulsed versions of 6N1P-I were produced with increased maximum electron emission at the cathode. - 6N2P
- double miniature low-frequency triode with high gain, functional analogue of 6N9S. An electrical analogue of the widely used 12AX7 lamp, but incompatible with it in terms of electrical pinout. - 6N3P
- double miniature high-frequency triode. It was widely used in domestic civilian radio receivers - VHF frequency conversion units were built on 6N3P. - 6N23P
- double miniature triode, functional analogue of ECC88. Designed for broadband high-frequency voltage amplification and industrial automation circuits. - 6N6P
,
6N30P
- double miniature triodes of medium power. Designed for amplification of low frequencies and operation in pulse circuits, as well as in push-pull low-power ULF output stages. 6N30P is probably the only Soviet lamp that has no foreign analogues, which is used in modern foreign industrial products. - 6N17B
- double small-sized low-power triode.
ULF printed circuit boards
You can assemble the ULF by surface mounting, or you can assemble it on printed circuit boards. The drawing of boards with lamps shows the method of connection with other elements of the amplifier (potentiometer, transformers). All connections are made using twisted pair, that is, a pair of tightly twisted wires. This should eliminate or at least reduce the induced noise in the wires.
It is based on a metal chassis. Behind the speaker transformers is a toroidal power transformer housed in a metal can that reduces line noise generated by the transformer.
The amplifier really plays warmly and somehow differently, it has a greater depth of sound, more volume. Although it only provides 2W of power, the sound is perfect for a small room!
Attention! Electronic devices are usually powered by 220 V. Mains voltage is dangerous, so use well-thought-out design solutions to avoid exposing yourself and other users to electric shock. Tube devices also contain high voltages. Make any adjustments only when the power source is turned off and after the high voltage capacitors have discharged. Lamps and some resistors reach high temperatures.
Due to their high input impedance, lamps are very sensitive to external interference. Therefore, use shielded cables. The metal connected to the amplifier body ground will protect the amplifier from picking up external noise.
- ULF CLASS D WITH RADIO TUBE
- HOMEMADE ULF PUSH-PULL
- TUBE FOR HOME AUDIO SYSTEM
- PREAMP FOR RECORD PLAYER
Current state
Currently, vacuum triodes have been almost completely replaced by semiconductor transistors. The exception is in areas where conversion of signals with a frequency of the order of hundreds of M - GHz of high power is required with a small number of active components, and dimensions and weight are not so critical, for example, in the output stages of radio transmitters. Powerful radio tubes have an efficiency comparable to powerful transistors; Their reliability is also comparable, but their service life is much shorter. Low-power triodes have low efficiency, since a significant part of the power consumed by the cascade is spent on incandescence, sometimes more than half of the total lamp consumption.
Also, some high-quality acoustic amplification equipment of the Hi-Fi and Hi-End classes is still made on the basis of lamps, despite the fact that the coefficient of nonlinear distortion recorded by the devices in almost any modern transistor devices is many times less than that of lamp devices. [ source not 3015 days specified
] Despite the high cost, such equipment is very popular among musicians and audiophiles due to its so-called “warmer”, “tube” sound, which is supposedly perceived by a person as more natural and closer to what it was when recording the original sound. A triode is a simple tube design that has a high gain, so it fits well into one of the principles of alternative audio engineering - the principle of minimalism, that is, the utmost simplicity of the equipment.