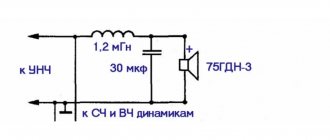
In the first part we talked about the essence, nature of sound, features of its distribution and perception. It's time to move on to devices that can reproduce this sound. The most common option to this day is a speaker. This device at one time caused a real revolution in the field of music engineering. Its fundamental simplicity and, at the same time, complexity of details are definitely worthy of close attention.
According to the principle of sound radiation, there is:
- electromagnetic
- electrodynamic
- electrostatic
- piezoelectric
- ionophone
- tape
- magnetoplanar
- isodynamic
- orthodynamic
- Hale emitter
You can read about all non-standard emitters using the links above. We will consider the design of a classic electrodynamic loudspeaker. The size of the driver determines the bandwidth in which the speaker will operate most effectively. Loudspeakers can be divided into 3 main types:
- low frequency
- mid-frequency
- high frequency
The appearance of the speaker
With the beginning of the active use of electricity, it became possible to transmit an audio signal, converting it into an electrical one and back. At different times, many methods of this transformation were invented. Among them are electrodynamic, electrostatic, isodynamic, tape, Hale emitter, piezo and even plasma emitter.
They operate on different physical principles and differ in the specific application. But the very first was still a device that implemented the electrodynamic principle. It remains the most common. Speaker, electrodynamic head, dynamic driver - all these terms are synonyms for the same invention.
On the left is Hans Oersted. On the right is the first commercial version of the electrodynamic driver (6-inch speaker, cost about $3000 in modern equivalent)
The physical principles on which the speaker works are based on electromagnetism, discovered by Hans Oersted and subsequently described by a whole galaxy of 19th-century physicists. The fact that a conductor carrying current is pushed out by a magnetic field, and in a conductor moving in this field, on the contrary, a current arises, actually led to the invention of the speaker.
The first device to employ all the basic design principles of a modern speaker was patented in 1898 by Oliver Lodge, after some thirty years of various attempts to find an effective implementation. And the speaker itself, in the form to which we are all accustomed, appeared approximately thirty years later.
Since then, the principles of its operation and basic design elements have remained unchanged. At the same time, and this is what is especially surprising, not a year goes by without information about the next revolutionary improvement in the speaker, allowing it to perform even better.
LF, MF and HF:
Woofers are usually larger than Ø200 mm and are designed to reproduce low frequencies (20-500 Hz). Midranges with a diameter of 75-165 mm and operate in the range of 100-7000 Hz. HF loudspeakers have a dome Ø25 mm (rarely a cone up to Ø100 mm) and are designed to reproduce frequencies above 1000 Hz. There are full range speakers, these are:
- broadband (with a single mobile system)
- coaxial (consists of several types of loudspeakers connected together)
Structurally, the speaker consists of a moving and magnetic system, and a frame that connects both units. The frame is sometimes missing when it comes to the tweeter, where it is a magnetic system with an upper decorative flange. According to the shape of the emitter (diffuser), the loudspeaker can be round, oval, square or ring in the case of HF.
Do-it-yourself paper speaker cone repair
Often, when operating speaker systems, the rules for their use are violated, which is why the speakers fail. How to fix a speaker cone. Speaker cone repair depends on the level of damage. Damage occurs when the material is not scratched through. Such a defect, during operation, is sure to turn into a through gap, which will quickly increase. Therefore, care must be taken to restore the material. To do this, use ordinary rubber glue, which is used to seal damaged rubber boats. A layer of glue is applied to the scratch on both sides and dried for 2-3 hours. The application of rubber glue should not be too thin. Then a second layer is applied. You need to apply more glue or do it in two steps. Final drying takes 48 hours, after which the speaker can be placed in the speaker system and turned on. Some aspects of DIY speaker cone repair are in the video.
Sectional view of a dome tweeter:
The photo below shows several types of speakers. Dome and cone are already familiar to us. Coaxial is exactly the same as classic, but with additional HF. Flat bass is also electrodynamic, but has a different design in order to have a minimum size (they are usually used in cars).
Purpose and scope of loudspeakers
A loudspeaker is a device that converts an electrical sound signal at the input into an audible acoustic signal at the output. To ensure proper quality, the loudspeaker must operate loudly and efficiently - reproduce the sound signal in the permissible (audible) dynamic (85-120dB) and frequency (200-5000Hz) ranges.
Loudspeakers have the widest application in various spheres of human activity: in industry, transport, sports, culture, and consumer services. For example, in industry, loudspeakers are used to provide public address communication (PAC), in transport - for emergency communications, announcements, in the domestic sphere - for paging alerts, as well as background music broadcasts. In the field of culture and sports, the most widely used are professional acoustic systems designed for high-quality musical accompaniment of events. Sound support systems (SSS) are built on the basis of such systems. Loudspeakers are actively used in a wide range of organizational measures to protect the population: in the field of security - in warning systems and evacuation control (SAEC), in the field of civil defense - in local warning systems (LSA) and are intended for direct (sound) warning of people in case of fire and emergency situations.
Basket (frame, diffuser holder)
A frame that holds the moving speaker system, connecting it to the magnetic system. A suspension is glued to the frame at the top, and a centering washer is attached to the bottom. A magnetic system is attached to the reverse side. Most often, frames are made of metal by stamping and painted. High-quality loudspeakers have aluminum frames and are manufactured using injection molding. There are also plastic baskets.
Read Me.
The navigation for this FAQ is as follows. All material is divided into parts, but at the same time, through the “Navigation” located at the top of any page, you can get to any point in this FAQ or return back.
This was done so that the overloaded page does not become overwhelming for people with a weak Internet connection or those who access the network via iPhone, iPod, etc.
As certain pages are published, the links in the navigation menu will become active.
This is my first time doing this, so there may be overlaps with addressing. Please report any errors you notice in the comments!
A few words about terminology.
A dynamic head, or loudspeaker head, or speaker for short, is an electromechanical device that converts changes in the strength and direction of electric current into sound waves. https://oldoctober.com/
A loudspeaker, or column, or Acoustic System (AS) is the acoustic design of the speakers or, more simply put, the box in which the speaker or speakers, if there are several, are mounted.
If there is more than one speaker and they are different, then the speaker is called multi-way. Speakers are conventionally divided into low-frequency (LF), mid-frequency (MF) and high-frequency (HF).
In this series of articles we will mainly talk about speaker repair. AS will be mentioned only in this connection.
There are several questions missing from Navigation, the answers to which I know.
- How to glue a magnet to flanges and at the same time center the core?
- How to make a dust cap?
- How to make a speaker hanger?
- How to make a diffuser?
- How to make a centering washer?
I doubt that these repair technologies are still relevant today, since most spare parts can be purchased separately. However, if the answers to any of these questions are of interest to DIYers, then I will try to answer them in detail, too, after I finish writing the main topics.
Return to top to "Navigation".
Emitter (diffuser, diaphragm)
It comes in conical, dome and even flat designs. The actual physical area that moves from the interaction of a voice coil with a permanent magnet, reproducing sound by compressing and rarefying air, thereby creating sound waves. If these are midrange or tweeter speakers, then the diffuser is a dome. In any case, the diffuser is connected to the suspension or is a single part with it. There are many materials from which diffusers are made ( Diffuser materials ):
- paper
- polypropylene
- carbon fiber
- Kevlar
- aluminum
- fabric or silk
- ceramics
Story
The day began with a short excursion into the history of the invention of the electrodynamics. Loudspeakers of a similar type were used back in the late 20s of the last century. Bell's telephone worked on a similar principle. It involved a membrane that moved in the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. These speakers had many serious shortcomings: frequency distortion, sound loss. To solve the problems associated with classic loudspeakers, Oliver Lorge proposed using his developments. Its coil moved across the power lines. A little later, two of his colleagues adapted the technology for the consumer market and patented a new design of electrodynamics, which is still used today.
Suspension (corrugated)
The hanger connects the top edge of the diffuser to the frame. Its type, material and rigidity directly affect the parameters of the loudspeaker. The powerful subwoofer heads are equipped with large suspensions with increased travel. In older loudspeakers, the surround and diffuser are made of paper and are a single unit. Basic forms of suspensions:
- toroidal (two-toroid, three-toroid)
- tangential
- s-shaped
- sawtooth
In addition, suspensions can have 2 and 3 waves, as well as variable thickness and wave shape. The shape can be different, this is determined by the purpose of the loudspeaker itself. If we divide the suspensions according to materials, then there are:
- rubber
- fabric
- paper
- polyurethane foam (foam)
- film
- metal
Table of contents
- 1. Purpose and scope of loudspeakers
- 2. Transformer loudspeakers
- 3. Speaker device
- 4. Horn loudspeaker device
- 5. Connecting transformer speakers
- 6. Classification of loudspeakers
- 7. Application area of loudspeakers
- 8. Speaker characteristics
- 8.1 Classification of loudspeakers by frequency response width
- 8.2 Classification of loudspeakers according to the width of the radiation pattern
- 8.3 Classification of loudspeakers by sound pressure
- 8.4 Classification of loudspeakers by design
- 9. Speaker placement
Centering washer (spider)
The main functions of the washer are to hold (center) the voice coil in a narrow magnetic gap and ultimately determine the rigidity of the moving system itself. They are mainly made of fabric with subsequent impregnation. To increase rigidity, double ones are used. For powerful subwoofers, flexible supply cords are laid on the washers. The washer is connected with glue to the voice coil. In old loudspeakers, such as 10GD-20 or 25GDN-5, the washer was made of textolite 1 mm thick and had a 3-lobe shape.
Cap
The cap is a shell made of synthetic or fabric, the main function of which is to protect the speakers from dust. In addition, the cap plays an important role in shaping a certain sound. In particular, when reproducing mid frequencies. For the purpose of the most rigid fastening, the caps are made round in shape, giving them a slight bend. As you probably already understood, the variety of materials is precisely related to achieving a certain sound. Fabrics with various impregnations, films, cellulose compositions and even metal meshes are used. The latter, in turn, also serve as a radiator. An aluminum or metal mesh conducts excess heat away from the coil.
Voice coil
It is wound with a single-core wire in insulation (varnish) on a cylindrical frame, which is placed in a magnetic gap. In most cases, voice coils are wound with a copper core in two layers. The tweeters have an aluminum core for less weight. The coil frame can be copper, aluminum, paper, polyimide or Kapton. As for the number of winding layers, it can have 2, 4, 6 or even 8 layers. The cross-section of the core has a round shape, but there are also flat, square and even hexagon-shaped cross-sections. If the coil has many layers, then some of them are wound on the inside, and some on the outside of the frame, this is due to the fastening of the cores and the distribution of heating.
How the speaker works - the lowdown
The appearance of the speaker
With the beginning of the active use of electricity, it became possible to transmit an audio signal, converting it into an electrical one and back. At different times, many methods of this transformation were invented. Among them are electrodynamic, electrostatic, isodynamic, tape, Hale emitter, Piezo and even plasma emitter.
They operate on different physical principles and differ in the specific application. But the very first was still a device that implemented the electrodynamic principle. It remains the most common. Speaker, electrodynamic head, dynamic driver
- all these terms are synonyms for the same invention.
On the left is Hans Oersted. On the right is the first commercial version of the electrodynamic driver (6-inch speaker, cost about $3000 in modern equivalent)
The physical principles on which the speaker works are based on electromagnetism, discovered by Hans Oersted and subsequently described by a whole galaxy of 19th-century physicists. The fact that a conductor carrying current is pushed out by a magnetic field, and in a conductor moving in this field, on the contrary, a current arises, actually led to the invention of the speaker.
The first device to employ all the basic design principles of a modern speaker was patented in 1898 by Oliver Lodge, after some thirty years of various attempts to find an effective implementation. And the speaker itself, in the form to which we are all accustomed, appeared approximately thirty years later.
Since then, the principles of its operation and basic design elements have remained unchanged. At the same time, and this is what is especially surprising, not a year goes by without information about the next revolutionary improvement in the speaker, allowing it to perform even better.
Speaker device
Any modern speaker includes a frame [1], which is also called a basket or even a spider. All other parts of the structure are supported on it.
A magnetic system is attached to the back of the basket, which consists of a ring magnet [2] and a magnetic core [3] - together they form an annular gap. This magnetic gap, the annular gap between two magnets, must be kept as small as possible to create the strongest possible magnetic field.
In the gap there is a so-called voice (sound) coil [4], which can perform reciprocating movements under the influence of a magnetic field, since an alternating current flows through it, corresponding in shape to the reproduced sound vibrations. It typically consists of wire coated with an insulating varnish and wound around a thin-walled cylinder called the voice coil frame [5].
It is attached to a diffuser [6] - a thin-walled structural element, which, when oscillating, actually reproduces sound. For this purpose, the diffuser must be able to move. For this purpose, so-called suspensions are installed [7, 8]: upper (outer) and lower. These are washers made of thin and flexible material with concentric bulges. Thanks to this shape, the suspensions allow the diffuser to move along the axis of symmetry of the entire structure back and forth.
He does this because he is pushed by a voice coil, which is subject to an electromagnetic force proportional to the strength of the alternating current that is supplied to the coil through flexible torque-free conductors [9]. On the other side, these wires end with terminals [10], to which the speaker cable coming from the amplifier is connected.
The picture is completed by a dustproof cap [11], which is attached to the diffuser at the front and, as the name implies, protects the magnetic gap from the penetration of dust particles into it.
The variety of speakers is enormous. They differ in power, operating range of reproduced frequencies, scope of application and many other parameters. Naturally, the technologies and materials used in the production of each part depend on this. We will consider them separately.
Diffuser
Initially, the diffuser was made of cellulose - paper or cardboard. The dust cap (if provided) was also made from the same material. Cellulose diffusers are still very often used today. The paper is good for its combination of lightness and rigidity. Moisture resistance, strength and durability are added to it by impregnation with synthetic materials.
In this sense, plastic is good, but a purely plastic non-composite diffuser has a number of disadvantages. To correct them, composite materials with a variety of components are used: from wood or glass fibers to Kevlar or even graphene. Metal diffusers have increased rigidity. Most often they are made from aluminum alloys.
Beryllium has some of the best parameters, but due to the increased cost of the material and its processing technologies, this option is quite expensive. In so-called dome tweeters, impregnated fabric is most often used, sometimes reinforcing a layer of the most rigid composite, with a hard filler, even diamond powder.
The most important requirements for a diffuser are a minimum of self-resonances and maximum rigidity, at which the “piston” mode of movement of the diffuser over its entire area becomes possible. These parameters must be combined with the most important requirements for the weight of the moving speaker system - it must be minimal. Thus, a high-quality diffuser is always a compromise of mutually conflicting conditions.
Speaker suspension
The inner (closest to the magnet) speaker suspension is also called a centering washer. Most often, this part is molded on a heated press from lightweight, tensile fabric with elastic synthetic impregnation - firmly and movably. Some high-power woofers use two centering washers, one behind the other.
With external suspension everything is a little more complicated. Initially, it was made in the form of concentric waves (corrugations) along the outer edge of a paper diffuser. This is what they do now in some cases, adding synthetic impregnation to the corrugation zone. For large vibration amplitudes, the external suspension is made of rubber, most often it is artificial butadiene rubber. The cross-section of the rubber suspension, in most cases, is a convex arc. There are options for “multi-wave” rubber suspensions, or the use of other profiles, including variable angles.
Both suspensions must ensure a strictly plane-parallel reciprocating movement of the entire moving speaker system with minimal deviations to the side from its axis.
Voice coil
This coil, operating in the magnetic gap of the speaker, is wound on a frame - a cylinder, which is often made of thick paper. Heat-resistant plastic is also used for the frame: Kapton, textolite, or other composite materials. For greater density and temperature stability (under heavy load, i.e. loudness, the coil heats up), aluminum-based alloys and even titanium are used.
The wire used to wind the voice coil is most often copper. Aluminum wire is lighter, and this is a plus in this case, but it has its drawbacks (higher electrical resistance with lower temperature stability) and is used less often. There is an option with bimetallic aluminum wire coated with copper, which improves conductivity.
For a denser arrangement of turns, the wire is sometimes made rectangular or hexagonal in cross-section. To obtain several options for coil resistance when connecting its parts in parallel or in series or using separate amplifiers, the voice coil, most often in low-frequency speakers, can be divided into separate sections wound on a common frame.
To better cool the voice coil, the magnetic gap in some tweeters is filled with a special liquid filled with fine magnetic powder. This increases system efficiency and improves heat dissipation.
Magnetic system
The efficiency of a speaker's magnetic system is determined primarily by the material of the magnet. The most common is ferrite. In the middle of the last century, magnets made of the AlNiCo (iron-aluminum-nickel-cobalt) alloy were common; in some cases, this option is still used. In recent historical periods, neodymium magnets have become increasingly widespread, creating a much stronger magnetic field. The problem here was obtaining a neodymium workpiece of the required size: neodymium is a difficult material to process. In addition, the cost of neodymium magnets has been rising recently.
Speaker basket
The most common and most technologically advanced version of the basket, or speaker frame, is a stamped part made of mild steel. Small frames can be made of plastic. A more advanced, durable and, most importantly, precise product in its geometry is produced by casting, most often from aluminum, followed by processing on metal-cutting machines.
It is important to understand: in order to achieve a minimum magnetic gap, the voice coil located in this gap must be made to move without touching its edges. To do this, its movement must be ideally coaxial with the magnetic gap along the entire possible amplitude of oscillations. The location of the coil in the magnetic gap must be perfectly symmetrical. This places high demands on the precision of manufacturing and assembly of all parts.
All speaker components are connected using glue using special equipment.
Each speaker, according to the materials and technologies used in it, dimensions, weight, electrical and mechanical parameters, has its own precisely defined purpose.
Source: stereo & video
Permanent magnet
A fixed DC magnet that is part of the magnetic system design. It attaches to the speaker frame, creating a stable magnetic flux through the annular gap that contains the voice coil. You can read about different magnets in the article: About magnets - alnico, ferrite, cobalt, neodymium . The shape can be different - ring, cylindrical (core) or a set of several small magnets. According to the use of materials for the magnet, it can be divided into:
- ferrite (ceramic)
- alnico
- samarium-cobalt
- neodymium
Magnetic system
The efficiency of a speaker's magnetic system is determined primarily by the material of the magnet. The most common is ferrite. In the middle of the last century, magnets made of the AlNiCo (iron-aluminum-nickel-cobalt) alloy were common; in some cases, this option is still used. In recent historical periods, neodymium magnets have become increasingly widespread, creating a much stronger magnetic field. The problem here was obtaining a neodymium workpiece of the required size: neodymium is a difficult material to process. In addition, the cost of neodymium magnets has been rising recently.
Faraday ring
Also called short-circuited turn. Installed externally on the core or on the inside of the top flange. The short-circuited turn effectively suppresses the influence of almost all sources of distortion in the loudspeaker. Reduces intermodulation and harmonics. With such a ring, the inductance of the voice coil is reduced, which automatically expands the reproduced frequency band upward.
Do-it-yourself speaker cone repair
Timely restoration of a damaged loudspeaker membrane will ensure its high-quality operation for a long time. Therefore, if wheezing and distortion begin to appear in the speaker system, first of all you need to carefully check the speaker cones. How to repair a speaker cone with your own hands. Minor damage is eliminated by applying rubber glue to the desired area, and larger defects are eliminated by applying a patch. To do this you need to do the following:
- Clean the gluing area from dust and dirt
- Use a sharp tool to cut off the overhanging edges of the tear
- Prepare a patch larger than the hole in size
- Coat the patch with glue and apply it to the back of the diffuser
As a patch, you can use newsprint, which is applied in 2-3 layers. If you use PVA glue, then you need to use office glue rather than construction glue. This completes the restoration of the speaker diffuser and after complete drying it can be installed in the speaker system.
Core, lower and upper flange
The iron around the magnet is the parts of the magnetic circuit. They form a working gap in a certain place and direct a concentrated magnetic flux there. Without them, the field near the voice coil will be highly scattered and the speaker will become ineffective. The dimensions of the “iron” flanges and core are calculated for the magnet to ensure an optimum between the dimensions of the magnetic system and the required magnetic field induction in a gap of a given size and configuration.
Core - transmits a magnetic field inside the coil, but should not be magnetized itself, therefore it is made of soft magnetic material. Sometimes there is a hole in the roll, it helps reduce the air pressure under the dust cap and cool the voice coil at high powers. Read more in the article - The influence of the hole in the speaker core .
A little about mobile speakers
Phone speakers are structurally different from “adult” models. It is unrealistic to place such a complex mechanism in a mobile case, so the engineers resorted to a trick and replaced a number of elements. For example, the coils have become stationary, and a membrane is used instead of a diffuser. Phone speakers are greatly simplified, so you shouldn’t expect high quality sound from them.
The frequency range that such an element can cover is significantly narrowed. In terms of its sound, it is closer to high-frequency devices, since there is no additional space in the phone body for installing thick magnetic cores.
The speaker design in a mobile phone differs not only in size, but also in its lack of independence. The device's capabilities are limited by software. This is done to protect the speaker structure. Many people remove this limit manually, and then ask the question: “Why do the speakers wheeze?”
The average smartphone has two of these elements. One is conversational, the other is musical. Sometimes they are combined to achieve a stereo effect. One way or another, it is possible to achieve depth and richness in sound only with a full-fledged stereo system.
Middle segment 1-2 thousand rubles
Pioneer TS1302i
The average cost is 1970 rubles.
View from all sides of the Pioneer TS1302i
The acoustics of this manufacturer will please car enthusiasts with a pleasant price, quality and design. If we consider the technical parameters, on individual points, these speakers are superior to any of the budget options proposed above, which is why their cost is higher.
Specifications:
| Number of stripes: | 2 pcs. |
| Resistance: | 4 ohm |
| Power Range (W): | 25 – nominal, 130 – maximum |
| Frequencies: | 50-27000 Hz |
| Sensitivity: | 90 dB |
Pioneer TS1302i
Advantages:
- Convenient installation;
- Acceptable price;
- Build quality;
- Sound.
Flaws:
- Not identified.
Flpine SXE-1325S
The average price is 1970 rubles.
Flpine SXE-1325S
An attractive speaker system at an affordable price for everyone, equipped with a neodymium and ferrite magnet, a titanium balanced dome tweeter, a foam surround and a long structured fiber cone.
Specifications:
| Bands: | 2 pcs. |
| Power, W): | 35 – nominal, 200 – maximum |
| Frequencies: | 70-20000 Hz |
| Sensitivity: | 92 dB |
| Manufacturer country: | China |
Flpine SXE-1325S
Advantages:
- The sound transmission is pleasing;
- Value for money;
- A worthy replacement for standard speakers;
- Midbass;
- High frequencies.
Flaws:
- Not identified.
EDGE EDST215-E6
Price: 1300 rubles.
EDGE EDST215-E6
The cone-shaped coaxial model is designed to enhance bass response and crystal-clear highs, driven by mid- and high-end PEI elements. The delivery of the product includes grilles and mounting screws.
Specifications:
| Installation depth: | 41 mm |
| Power range: | 50-100 W |
| Resistance: | 4 ohm |
| Bands: | 2 pcs. |
| Frequencies: | 80-20000 Hz |
EDGE EDST215-E6
Advantages:
- Powerful;
- Sound clarity;
- Build quality;
- Design;
- Unique lightweight IMPP cone;
- Suitable for almost every car.
Flaws:
- Not identified.
MRM-POWER MR-GTF1365
The average cost is 1270 rubles.
Equipment MRM-POWER MR-GTF1365
The speakers, available in black with a full mounting kit, provide excellent sound quality, are easy and quick to install, and are made of durable materials that ensure a long service life.
Specifications:
| Type: | coaxial |
| Rated and maximum power: | 600 W |
| Number of stripes: | 3 pcs. |
| Resistance: | 4 ohm |
| Sensitivity: | 90 dB |
| Frequency range: | 86-20000 Hz |
| Manufacturer country: | China |
MRM-POWER MR-GTF1365
Advantages:
- Pure sound transmission;
- High quality;
- Equipment;
- Easy to install;
- Price.
Flaws:
- Not identified.
JVC CS-V518
The average cost is 1860 rubles.
JVC CS-V518 speaker system design
The stylish speakers are made from durable materials and are well constructed. They will allow you to enjoy high-quality sound for a long time.
Specifications:
| Number of stripes: | 1 PC. |
| Sensitivity: | 90 dB |
| Weight: | 450 g |
| Power, W): | 25 – nominal, 200 – maximum |
| Frequency limits (Hz): | 25 – lower, 20000 – upper |
| Resistance: | 4 ohm |
JVC CS-V518
Advantages:
- Value for money;
- Volume;
- Design.
Flaws:
- Low frequencies.
Horn loudspeaker device
The horn loudspeaker is the (active primary) means of reproducing the audio acoustic signal in the permissible frequency and dynamic ranges. The characteristic features of the horn are the provision of high acoustic sound pressure due to a limited opening angle and a relatively narrow frequency range. Horn loudspeakers are used mainly for voice announcements and are widely used in places with high noise levels - underground parking lots, bus stations. Highly concentrated (narrowly directed) sound allows them to be used on railways. stations, in subways. Most often, horn loudspeakers are used for sounding open areas - parks, stadiums.
A horn loudspeaker (horn) is a matching element between the driver (emitter) and the environment. The driver, rigidly connected to the horn, converts the electrical signal into sound energy, which is received and amplified in the horn. The sound energy inside the horn is amplified due to a special geometric shape that provides a high concentration of sound energy. The use of an additional concentric channel in the design makes it possible to significantly reduce the size of the horn while maintaining quality characteristics.
The horn consists of the following parts (see figure, picture taken from the Internet):
- metal diaphragm (a);
- voice coil or ring (b);
- cylindrical magnet (c);
- compression driver (d);
- concentric channel or projection (e);
- megaphone or bugle (f).
A horn loudspeaker works as follows: an electrical sound signal is fed to the input of a compression driver (d), which converts it into an acoustic signal at the output. The driver is (rigidly) attached to the horn (f) providing high sound pressure. The driver consists of a rigid metal diaphragm (a) driven (excited) by a voice coil (coil or ring b) wound around a cylindrical magnet (c). The sound in this system propagates from the driver, passing through a concentric channel (e), is exponentially amplified in the horn (f), and then goes to the output.
NOTE: In various literature and depending on the context, the following names of the horn may be found - megaphone, bugle, loudspeaker, reflector, trumpet.
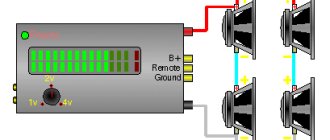
Connecting transformer speakers
In broadcast systems, the most common option is when several transformer loudspeakers need to be connected to one broadcast amplifier, for example, to increase volume or coverage area.
If you have a large number of speakers, it is most convenient to connect them not directly to the amplifier, but to a line, which in turn is connected to the amplifier or switch (see figure).
The length of such lines can be quite long (up to 1 km). Several such lines can be connected to one amplifier, and the following rules must be observed:
RULE 1
: Transformer speakers are connected to the broadcast amplifier (only) in parallel.
RULE 2
: The total power of all loudspeakers connected to the broadcast amplifier (including through the relay module) should not exceed the rated power of the broadcast amplifier.
For convenience and reliability of connection, it is necessary to use special terminal blocks.
Transformer loudspeakers
Transformer loudspeakers - loudspeakers with a built-in transformer are the final executive elements in wired broadcast systems, on the basis of which fire warning systems, local warning systems, and public address systems are built. In such systems, the principle of transformer matching is implemented, in which a separate loudspeaker or a line with several loudspeakers is connected to the high-voltage output of the broadcast amplifier. Signal transmission in a high-voltage line allows you to maintain the amount of transmitted power by reducing the current component, thereby minimizing losses on the wires. In a transformer loudspeaker, there are 2 stages of conversion. At the first stage, a transformer is used to reduce the voltage of the high-voltage audio electrical signal; at the second stage, the electrical signal is converted into an audible acoustic sound signal.
The illustration shows the back of a cabinet wall-mount transformer loudspeaker. The transformer loudspeaker consists of the following parts:
The loudspeaker housing, depending on the application, can be made of various materials, the most widespread of which today is ABC plastic. The housing is necessary for ease of installation of the loudspeaker, protection of live parts from dust and moisture, improvement of acoustic characteristics, and formation of the required directivity pattern (NDP).
The step-down transformer is designed to lower the high-voltage voltage of the input line (15/30/60/120V or 25/75/100V) to the operating voltage of the electrodynamic converter (speaker). The primary winding of a transformer can contain multiple taps (e.g., full power, 2/3 power, 1/3 power), allowing the power output to vary. The taps are marked and connected to the terminal blocks. Thus, each such tap has its own impedance (r, Ohm) - reactance (of the primary winding of the transformer) depending on frequency. By choosing (knowing) the impedance value, you can calculate the power (p, W) of the loudspeaker at various voltages (u, V) of the input broadcast line, as:
p = u2/r
The terminal block provides convenience for connecting the broadcast line to various taps of the primary winding of the transformer loudspeaker.
Speaker is a device for converting an electrical signal at the input into an audio (audible) acoustic signal at the output. Connects to the secondary winding of the step-down transformer. In a horn loudspeaker, the role of the speaker is played by a driver rigidly attached to the horn.